简介
前篇文章分析了下Aria2 出现cpu爆满的情况,最主要的区别是换成了utp之后,包的大小变小了,由原本tcp的64k变成了utp的1k,加上utp有丢包重传的机制,导致下载相同数据的时候,utp包的数量为tcp的200倍,加上原本这个框架为epoll机制,当有数据到来的时候,epoll就没有机会休眠,换成utp之后,epoll触发的概率就大了很多,在网络不好的情况下,epoll基本没有超时的机会,导致一直循环,所以cpu爆满又因为 原本为单线程的方式,处理数据又慢,所以最先想到的就是多线程的方式,既然cpu没有时间休息,我们可以让主线程每个轮休都让它休息,然后任务交给子线程来处理,这样就可以做到cpu可以减低任务又处理的快
下面分析下要解决的问题:
1.更改当前的架构思维
2.Bt只有一个端口,udp方式监听这个端口只能得到一个socketfd,那么一个socketfd在多线程中怎么解决
3.utp并不是线程安全的
更改当前的架构思维
Linux 高性能编程中有一个Reactor 模式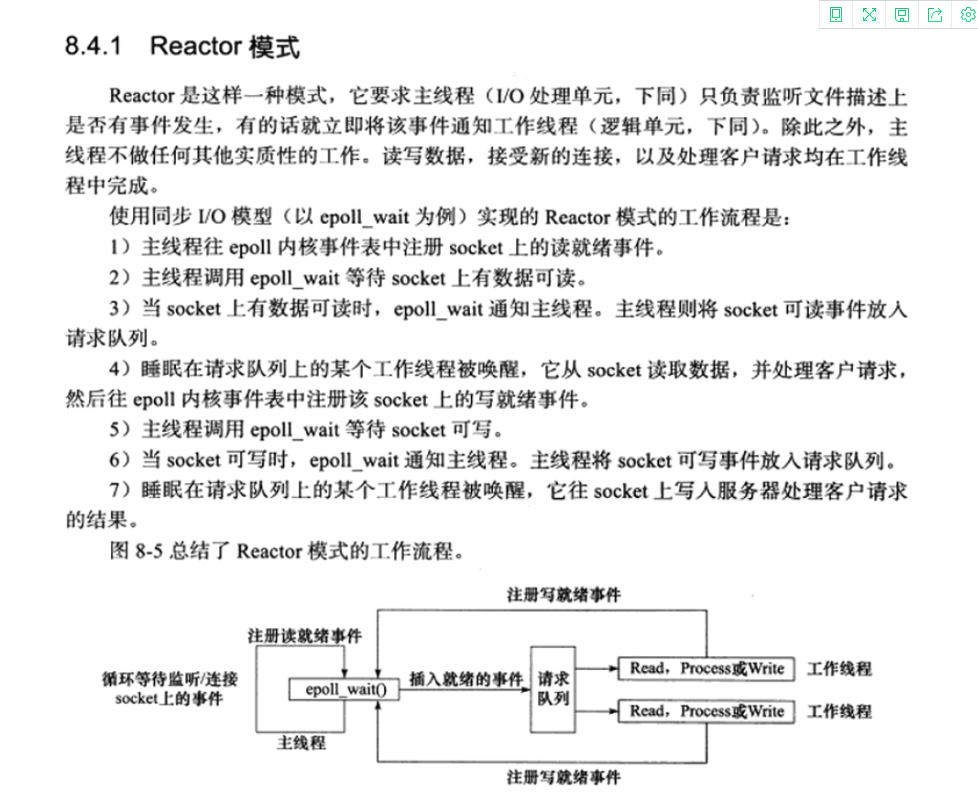
关于Reactor 模式可以参考这个链接
https://blog.csdn.net/analogous_love/article/details/53319815
也即是主线程创建epoll用于监听socketfd是否有事件到来,如果有就交给子线程来处理,所以我们的主线程可以这样写
//引擎开始运行 这边参数为true
int DownloadEngine::run(bool oneshot)
{
GlobalHaltRequestedFinalizer ghrf;
//如果 commands_ 或者 routineCommands_ 队列不为空,commands_一开始就有添加了一个保持事件响应的引用对象KeepRunningCommand 所以不为空
while (!commands_.empty() || !routineCommands_.empty() || !canExit()) {
noWait_ = false;
//重置时钟
global::wallclock().reset();
//每次主线程都休眠10毫秒
usleep(1000);
//计算下载的速度状态等,用来显示在输出控制台上
//calculateStatistics();
{
//1.std::lock_guard 在构造函数中进行加锁,析构函数中进行解锁。
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mutex_);
if(!commands_.empty()){
waitData();
}
//判断是否达到了刷新界面的时间,constexpr auto A2_DELTA_MILLIS = std::chrono::milliseconds(10);
if (lastRefresh_.difference(global::wallclock()) + A2_DELTA_MILLIS >= refreshInterval_) {
//刷新的间隔为1秒
refreshInterval_ = DEFAULT_REFRESH_INTERVAL;
//保存上一次刷新的时间
lastRefresh_ = global::wallclock();
//执行命令 ,状态为 Command::STATUS_ALL
executeCommand(commands_, Command::STATUS_ALL);
} else {
//如果还没有到刷新的时间,执行命令,状态为 Command::STATUS_ACTIVE
executeCommand(commands_, Command::STATUS_ACTIVE);
}
//执行命令
executeCommand(routineCommands_, Command::STATUS_ALL);
}
//判断是否接受到了退出的信号处理
afterEachIteration();
if (!noWait_ && oneshot) {
return 1;
}
}
//如果到了这里,就说明引擎已经开始停止
onEndOfRun();
return 0;
}
void DownloadEngine::executeCommand(std::deque<std::unique_ptr<Command>>& commands,Command::STATUS statusFilter){
size_t max = commands.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < max; ++i) {
//遍历每一个commands命令
auto com = std::move(commands.front());
commands.pop_front();
//判断他们的状态
if (!com->statusMatch(statusFilter)) {
com->clearIOEvents();
commands.push_back(std::move(com));
continue;
}
/*if(com->getRunningCommandPid() == 2){
LOGD("DownloadEngine executeCommand command name %s commit Thread %d",com->getCommandName().c_str(),com->getRunningCommandPid());
}*/
//改变当前command的命令状态为 STATUS_INACTIVE
com->transitStatus();
//往线程池中提交任务
threadPool_->commit(com->getRunningCommandPid(), execFunc, std::move(com));
}
}
可以看到主线程只是通过调用waitData来通过epoll监听socketfd是否有事件发生,如果有就调用 executeCommand 来将这个任务交给线程池处理
udp监听一个端口怎么样解决多个线程之间共享的问题
其实对于这个问题,如果是单个socketfd来说的话,处理起来是很复杂的,很容易发生数据的混乱,比如同时发送,同时接收数据等,所以换个思路,我们是否可以通过监听一个udp的端口得到多个socketfd而这个其实linux 在3.9之后就有选项支持的,既是创建socketfd的时候通过设置 SO_REUSEPORT ,下面是关于介绍 https://lwn.net/Articles/542629/
下面是具体的demo ,首先是服务端的代码实现
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<netinet/in.h>
#include<arpa/inet.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<netdb.h>
#include<stdarg.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<string>
#include<sys/syscall.h>
using namespace std;
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
string g_ip;
unsigned short g_port;
pid_t gettid()
{
return syscall(SYS_gettid);
}
inline string IpU32ToString(unsigned ipv4)
{
char buf[INET_ADDRSTRLEN] = {0};
struct in_addr in;
in.s_addr = ipv4;
if(inet_ntop(AF_INET, &in ,buf, sizeof(buf)))
{
return string(buf);
}
else
{
return string("");
}
}
void start_udp_server(string &ip, unsigned port){
cout << "ip: " << ip << " " << port << " " << gettid() << endl;
struct sockaddr_in server_addr;
socklen_t server_addr_length = sizeof(server_addr);
//bzero(&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip.c_str());
server_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
int server_socket_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if(server_socket_fd < 0)
{
perror("Create Socket Failed:");
exit(1);
}
int opt_val = 1;
setsockopt(server_socket_fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEPORT, &opt_val, sizeof(opt_val));
if(-1 == (bind(server_socket_fd,(struct sockaddr*)&server_addr,sizeof(server_addr))))
{
perror("Server Bind Failed:");
exit(1);
}
while(1){
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
socklen_t client_addr_length = sizeof(client_addr);
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
bzero(buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
cout << "begin to recv data ..." << " " << gettid() << endl;
int res = recvfrom(server_socket_fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE,0,(struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, &client_addr_length);
if(res == -1)
{
perror("Receive Data Failed:");
exit(1);
}
cout << "recv " << res << " bytes from " << IpU32ToString(client_addr.sin_addr.s_addr) << ":" << server_addr.sin_port << " " << gettid() << endl;
res = sendto(server_socket_fd, buffer, res, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr,sizeof(client_addr));
if(res < 0)
{
perror("Send File Name Failed:");
exit(1);
}
cout << "response " << res << " bytes to client." << " " << gettid() << endl;
}
}
void* thread_func(void* arg){
start_udp_server(g_ip, g_port);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
if (argc < 4) {
cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <local_ip> <udp_port> <thread_count>"<< endl;
exit(0);
}
g_ip = argv[1];
g_port = atoi(argv[2]);
int thread_count = atoi(argv[3]);
cout << "ip: " << g_ip << " port: " << g_port << " thread_cout: " << thread_count << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < thread_count; i++){
pthread_t thread_fd;
pthread_create(&thread_fd, NULL, &thread_func, NULL);
}
while(1){
sleep(3600);
}
return 0;
}
接下来是客户端的代码实现
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<netinet/in.h>
#include<arpa/inet.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<netdb.h>
#include<stdarg.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define SERVER_PORT 8000
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
inline unsigned IpStringToU32(const char* pAddr) {
in_addr in = { 0 };
if (inet_pton(AF_INET, pAddr, &in) > 0) {
return in.s_addr;
}
return 0;
}
inline unsigned IpStringToU32(const string& strAddr) {
return IpStringToU32(strAddr.c_str());
}
inline string IpU32ToString(unsigned ipv4) {
char buf[INET_ADDRSTRLEN] = { 0 };
struct in_addr in;
in.s_addr = ipv4;
if (inet_ntop(AF_INET, &in, buf, sizeof(buf))) {
return string(buf);
} else {
return string("");
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc < 3) {
cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <server ip> <server port> " << endl;
exit(0);
}
string server_ip = argv[1];
unsigned short port = atoi(argv[2]);
cout << "server_ip: " << server_ip << " " << port << endl;
struct sockaddr_in server_addr, client_addr;
socklen_t client_addr_length = sizeof(client_addr);
bzero(&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(server_ip.c_str());
server_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
int client_socket_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (client_socket_fd < 0) {
perror("Create Socket Failed:");
exit(1);
}
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
int len = BUFFER_SIZE;
int i = 1;
int max = 10;
cout << "please input the number of sending pkg " << endl;
cin >> max;
cout << " send to " << IpU32ToString(server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr) << " port " << ntohs(server_addr.sin_port) << endl;
int res = sendto(client_socket_fd, buf, len, 0, (struct sockaddr*) &server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
if (res < 0) {
perror("send to relay fail:");
exit(1);
}
cout << "send " << res << " bytes to relay server " << IpU32ToString(server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr) << " "<< ntohs(server_addr.sin_port) << "waiting for response..." << endl;
close(client_socket_fd);
return 0;
}
经过测试发现,当使用 SO_REUSEPORT 之后,内核会通过四元组的方式hash得到唯一确定的socketfd,所以对于一个连接socketfd来说,并不会出现数据的混乱,除非这个socketfd主动的关闭掉了,这样内部的socketfd又要重新的调整了,而且经过我的测试发现创建socketfd 可以在一个线程中准备好所有的socketfd,然后在每个子线程执行接收发送都是可行的,使用这个属性可以做到cpu的负载均衡
utp线程安全的实现
libutp线程不安全,utp.cpp中有很多全局数据,例如_global_stats, g_rst_infos, g_utp_sockets。因此不建议在多线程程序中使用,如果使用的话,在API使用前加锁进行同步,注意这里加锁不能加在utp的回调函数里面,一般我们主动调用的函数都要加锁,但是utp的回调函数不用加锁,因为很多回调函数都是因为我们主动调用触发的,重复的加锁,会造成死锁,单个utp锁的就不展示了,我们要考虑的是多个utp锁的实现,这样锁的粒度会更小,utp库里面有一个utp_context 对象,内部维护了一个utpSocket集合,所以我们可以尝试的给每个线程创建一个utp_context 对象,在这个对象里面在设置对应的锁
服务端的代码实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define a2_sockopt_t void*
#ifdef __linux__
#include <linux/errqueue.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#endif
#include "utp.h"
#include<pthread.h>
char *o_remote_address;
char* o_remote_port;
utp_context *ctx_a;
utp_socket *s_a;
utp_context *ctx_b;
utp_socket *s_b;
int fd_a,fd_b;
int quit_flag;
/*保证存取操作的原子性 互斥性*/
pthread_mutex_t mut_a;
pthread_mutex_t mut_b;
//强制退出的信号处理函数
void handler(int number)
{
printf("caught signal close_utp \n");
quit_flag = 1;
}
//utp库真正发送的逻辑
uint64 callback_sendto_a(utp_callback_arguments *a)
{
struct sockaddr_in *sin = (struct sockaddr_in *) a->address;
printf("sendto: %zd byte packet to %s:%d%s\n", a->len, inet_ntoa(sin->sin_addr), ntohs(sin->sin_port),(a->flags & UTP_UDP_DONTFRAG) ? " (DF bit requested, but not yet implemented)" : "");
sendto(fd_a, a->buf, a->len, 0, a->address, a->address_len);
return 0;
}
//收到了客户端发送的数据
uint64 callback_on_read_a(utp_callback_arguments *a)
{
const unsigned char *p;
ssize_t len, left;
left = a->len;
p = a->buf;
while (left) {
len = write(STDOUT_FILENO, p, left);
left -= len;
p += len;
printf("Wrote %lu bytes, %lu left\n", len, left);
}
utp_read_drained(a->socket);
//随后写数据
utp_write(s_a, "000", 4);
return 0;
}
//utp 收到了客户端的连接
uint64 callback_on_accept_a(utp_callback_arguments *a)
{
assert(!s_a);
s_a = a->socket;
printf("callback_on_accept inbound socket %p state %d \n ", s_a,utp_get_status(s_a));
//发送数据
utp_write(s_a, "000", 4);
return 0;
}
//utp库真正发送的逻辑
uint64 callback_sendto_b(utp_callback_arguments *a)
{
struct sockaddr_in *sin = (struct sockaddr_in *) a->address;
printf("sendto: %zd byte packet to %s:%d%s\n", a->len, inet_ntoa(sin->sin_addr), ntohs(sin->sin_port),(a->flags & UTP_UDP_DONTFRAG) ? " (DF bit requested, but not yet implemented)" : "");
sendto(fd_b, a->buf, a->len, 0, a->address, a->address_len);
return 0;
}
//收到了客户端发送的数据
uint64 callback_on_read_b(utp_callback_arguments *a)
{
const unsigned char *p;
ssize_t len, left;
left = a->len;
p = a->buf;
while (left) {
len = write(STDOUT_FILENO, p, left);
left -= len;
p += len;
printf("Wrote %lu bytes, %lu left\n", len, left);
}
utp_read_drained(a->socket);
return 0;
}
//utp 收到了客户端的连接
uint64 callback_on_accept_b(utp_callback_arguments *a)
{
assert(!s_b);
s_b = a->socket;
printf("callback_on_accept inbound socket %p state %d \n ", s_b,utp_get_status(s_b));
//发送数据
utp_write(s_b, "000", 4);
return 0;
}
//子线程执行的逻辑
void *processData_a(void *param) {
struct addrinfo hints, *res;
int error;
fd_a = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP);
if (fd_a < 0){
printf("processData create Socket fail return");
return NULL;
}
int sockopt = 1;
//udp .这里设置属性为 SO_REUSEPORT, 允许一个端口同时有多个fd 支持
if (setsockopt(fd_a, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEPORT, (a2_sockopt_t)&sockopt, sizeof(sockopt)) < 0) {
printf("SocketCore setsockopt SO_REUSEPORT failed \n");
close(fd_a);
return NULL;
}
memset(&hints, 0, sizeof(hints));
hints.ai_family = AF_INET;
hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_DGRAM;
hints.ai_protocol = IPPROTO_UDP;
if ((error = getaddrinfo(o_remote_address, o_remote_port, &hints, &res))){
printf("getaddrinfo: %s\n", gai_strerror(error));
return NULL;
}
if (bind(fd_a, res->ai_addr, res->ai_addrlen) != 0){
printf("bind fail return NULL");
return NULL;
}
freeaddrinfo(res);
ctx_a = utp_init(2);
assert(ctx_a);
//设置对应的回调函数
utp_set_callback(ctx_a, UTP_SENDTO, &callback_sendto_a);
utp_set_callback(ctx_a, UTP_ON_READ, &callback_on_read_a);
utp_set_callback(ctx_a, UTP_ON_ACCEPT, &callback_on_accept_a);
while (!quit_flag) {
unsigned char socket_data[4096];
struct sockaddr_in src_addr;
socklen_t addrlen = sizeof(src_addr);
ssize_t len;
//printf("thread_a begin to recv data .. \n");
len = recvfrom(fd_a, socket_data, sizeof(socket_data), MSG_DONTWAIT, (struct sockaddr *)&src_addr, &addrlen);
if (len < 0) {
if (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EWOULDBLOCK) {
utp_issue_deferred_acks(ctx_a);
} else {
printf("recvfrom data len < 0 \n");
}
}else{
printf("thread_a recv data len %lu \n",len);
//将收到的数据交给utp库处理
if (!utp_process_udp(ctx_a, socket_data, len,(struct sockaddr *) &src_addr, addrlen)) {
printf("UDP packet not handled by UTP. Ignoring.\n");
}
}
if(s_a){
//随后写数据
utp_write(s_a, "000", 4);
}
}
return NULL;
}
void *processData_b(void *param) {
struct addrinfo hints, *res;
int error;
fd_b = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP);
if (fd_b < 0){
printf("processData create Socket fail return");
return NULL;
}
int sockopt = 1;
//udp .这里设置属性为 SO_REUSEPORT, 允许一个端口同时有多个fd 支持
if (setsockopt(fd_b, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEPORT, (a2_sockopt_t)&sockopt, sizeof(sockopt)) < 0) {
printf("SocketCore setsockopt SO_REUSEPORT failed \n");
close(fd_a);
return NULL;
}
memset(&hints, 0, sizeof(hints));
hints.ai_family = AF_INET;
hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_DGRAM;
hints.ai_protocol = IPPROTO_UDP;
if ((error = getaddrinfo(o_remote_address, o_remote_port, &hints, &res))){
printf("getaddrinfo: %s\n", gai_strerror(error));
return NULL;
}
if (bind(fd_b, res->ai_addr, res->ai_addrlen) != 0){
printf("bind fail return NULL");
return NULL;
}
freeaddrinfo(res);
ctx_b = utp_init(2);
assert(ctx_b);
//设置对应的回调函数
utp_set_callback(ctx_b, UTP_SENDTO, &callback_sendto_b);
utp_set_callback(ctx_b, UTP_ON_READ, &callback_on_read_b);
utp_set_callback(ctx_b, UTP_ON_ACCEPT, &callback_on_accept_b);
while (!quit_flag) {
unsigned char socket_data[4096];
struct sockaddr_in src_addr;
socklen_t addrlen = sizeof(src_addr);
ssize_t len;
//printf("thread_b begin to recv data .. \n");
len = recvfrom(fd_b, socket_data, sizeof(socket_data), MSG_DONTWAIT, (struct sockaddr *)&src_addr, &addrlen);
if (len < 0) {
if (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EWOULDBLOCK) {
utp_issue_deferred_acks(ctx_b);
} else {
printf("recvfrom data len < 0 \n");
}
}else{
printf("thread_b recv data len %lu \n",len);
//将收到的数据交给utp库处理
if (!utp_process_udp(ctx_b, socket_data, len,(struct sockaddr *) &src_addr, addrlen)) {
printf("UDP packet not handled by UTP. Ignoring.\n");
}
}
if(s_b){
//随后写数据
utp_write(s_b, "000", 4);
}
}
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//远程要监听的ip和端口号
o_remote_address = "0.0.0.0";
o_remote_port = "8888";
struct sigaction sigIntHandler;
//设置强制退出的信号处理函数
sigIntHandler.sa_handler = handler;
sigemptyset(&sigIntHandler.sa_mask);
sigIntHandler.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(SIGINT, &sigIntHandler, NULL);
pthread_t thread_fd1;
pthread_create(&thread_fd1, NULL, &processData_a,NULL);
pthread_t thread_fd2;
pthread_create(&thread_fd2, NULL, &processData_b, NULL);
//主线程等待子线程
pthread_join(thread_fd1,NULL);
pthread_join(thread_fd2,NULL);
return 0;
}
正常情况下会出现这个问题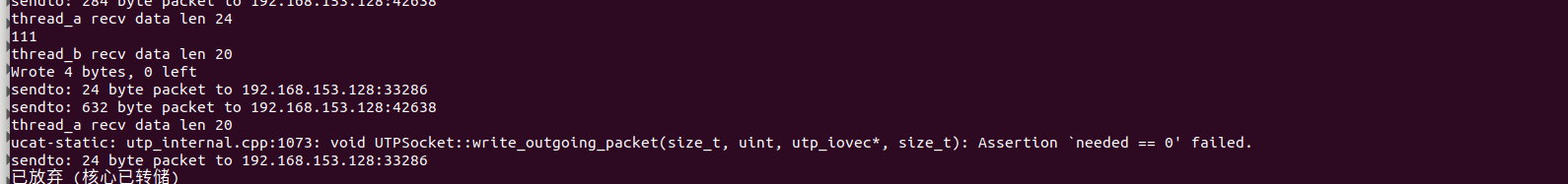
这是因为utp这个库里面含有静态成员变量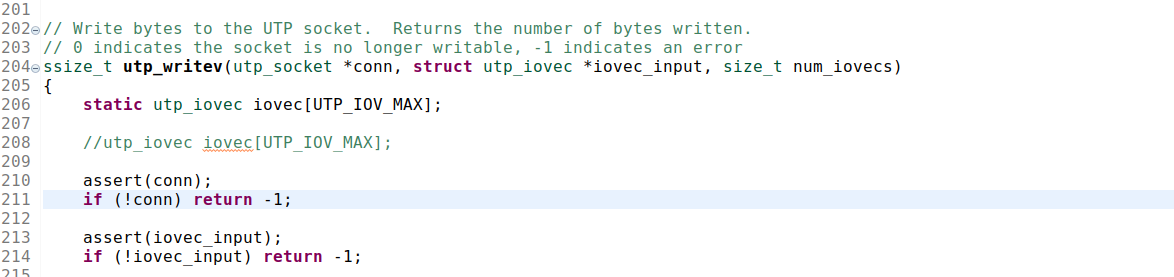
将这个static 去掉就可以解决这个问题,也就可以做到多个utp_context 是共享的
项目的实现
对于Bt这部分来说,我准备开启三个线程,也即是要创建三个utp_context 对象,创建3个sockfd,这里要注意这里要维护俩个集合,一个是关于utp_context 的集合,一个是关于socketfd的集合比如,客户端随机的获取到一个utp_context 对象,创建utp_socket ,执行连接的操作,对于客户端来说,下次接收数据的时候,怎么样找到这个utp_context 对象,所以要维护这个集合关于第二个集合是这样的 当使用了SO_REUSEPORT 属性之后,客户端随便使用一个socketfd用于发送消息,但是对于消息的接收,是随机的,也即是消息的到来并不是客户端的这个socketfd,所以要维护这个集合
关于utp_context 的集合
/*
* GlobalUtpMapping.h
*
* Created on: 2019年10月21日
* Author: yuhui
*/
#ifndef SRC_GLOBALUTPMAPPING_H_
#define SRC_GLOBALUTPMAPPING_H_
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <mutex>
#include <deque>
#include <libutp/utp.h>
#include <memory>
namespace aria2 {
class GlobalUtpMapping {
private:
// 因为 set 容器中所有元素都是唯一的,所以使用这个集合可以保证元素是唯一的
std::map<std::pair<std::string, uint16_t>,utp_context*> mapUtpContext;
//用于随机的获取到一个utp_context 对象
std::deque<utp_context*> utpContextDeque_;
//线程互斥锁
mutable std::mutex mutex_;
public:
~GlobalUtpMapping();
//根据指定的ip和端口号得到对应的utp_context 对象
utp_context* getUtpContext(std::string addr,uint16_t port);
//将对应的端口号跟ip对应起来
void putContext(std::string addr,uint16_t port,utp_context* context,int postion,std::string commmadName);
//将当前对应的ip和端口号,从集合里面移除出去
bool deleteAddr(std::string addr,uint16_t port,int position);
//添加UtpContextUserData 到
void addUtpContext(utp_context* context);
//随机的获取到一个 utp_context 对象
utp_context* getRandomUtpContext();
};
}
#endif /* SRC_GLOBALUTPMAPPING_H_ */
#include "GlobalUtpMapping.h"
#include "m4399_log.h"
namespace aria2 {
GlobalUtpMapping::~GlobalUtpMapping(){
mapUtpContext.clear();
utpContextDeque_.clear();
LOGD("GlobalUtpMapping 虚构函数的执行");
}
//根据指定的ip和端口号得到对应的utp_context 对象
utp_context* GlobalUtpMapping::getUtpContext(std::string addr,uint16_t port){
//std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mutex_);
auto i = mapUtpContext.find(std::make_pair(addr, port));
if (i == mapUtpContext.end()) {
return NULL;
}
return (*i).second;
}
void GlobalUtpMapping::putContext(std::string addr,uint16_t port,utp_context* context,int position,std::string commandName){
//1.std::lock_guard 在构造函数中进行加锁,析构函数中进行解锁。
//std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mutex_);
auto i = mapUtpContext.find(std::make_pair(addr, port));
if (i == mapUtpContext.end()) {
mapUtpContext[std::make_pair(addr, port)] = context;
LOGD("GlobalUtpMapping putConnection commandName %s first Add addr %s port %d position %d",commandName.c_str(),addr.c_str(),port,position);
}else{
if((*i).second == context){
return;
}
mapUtpContext[std::make_pair(addr, port)] = context;
LOGD("GlobalUtpMapping putConnection commandName %s update addr %s port %d position %d",commandName.c_str(),addr.c_str(),port,position);
}
}
//将当前对应的ip和端口号,从集合里面移除出去
bool GlobalUtpMapping::deleteAddr(std::string addr,uint16_t port,int postion){
//1.std::lock_guard 在构造函数中进行加锁,析构函数中进行解锁。
//std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mutex_);
mapUtpContext.erase(std::make_pair(addr, port));
LOGD("UtpContextUserData deleteAddr addr %s port %d position %d",addr.c_str(),port,postion);
return false;
}
//添加UtpContextUserData 到 utpContextMap_ 集合中,默认状态为没有使用状态
void GlobalUtpMapping::addUtpContext(utp_context* contextUserData){
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mutex_);
utpContextDeque_.push_back(contextUserData);
}
//随机的获取到一个utp_context 对象
utp_context* GlobalUtpMapping::getRandomUtpContext(){
if(utpContextDeque_.empty()){
return NULL;
}
//如果到了这里就说明全部都已经使用了,随机的获取一个
int index = rand() % 3;
index = index < 0 ? 0 :index;
index = index == 3 ? index -1 : index;
//LOGD("DownloadEngine::getUnusedUtpContext() rand == %d",index);
return utpContextDeque_[index];
}
}
关于socketfd 的集合
#ifndef ARIA2LIBANDROIDPROJECT_UTPCONTEXTUSERDATA_H
#define ARIA2LIBANDROIDPROJECT_UTPCONTEXTUSERDATA_H
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <mutex>
#include "SocketCore.h"
#include <deque>
namespace aria2 {
class DownloadEngine;
//utp userData封装
class UtpContextUserData {
//用来存储 socketCore 对应的 ip和端口号的集合
// 因为 set 容器中所有元素都是唯一的,所以使用这个集合可以保证元素是唯一的
std::map<std::pair<std::string, uint16_t>,std::shared_ptr<SocketCore>> mapSocket;
//客户端用于主动连接的socket
std::shared_ptr<SocketCore> socketCore_;
//持有DownloadEngine 指针
DownloadEngine *downloadEngine;
//线程互斥锁
mutable std::mutex mutex_;
//针对当前utp_context 的 互斥锁
mutable std::mutex utpContextMutex_;
//标识是哪个
int position_;
public:
//初始化函数
void init(DownloadEngine * engine,int position);
//获取到DownloadEngine 对象
DownloadEngine* getDownloadEngine();
//根据指定的ip和端口号得到对应的连接对象
std::shared_ptr<SocketCore> getConnection(std::string addr,uint16_t port);
//将对应的端口号跟ip对应起来
void putConnection(std::string addr,uint16_t port,std::shared_ptr<SocketCore> conn,std::string commandName);
//将当前对应的ip和端口号,从集合里面移除出去
bool deleteAddr(std::string addr,uint16_t port);
//客户端随机的从队列里面获取到一个发送数据的SocketCore对象
std::shared_ptr<SocketCore> clientGetConnection();
//添加socketCore 到队列中
void setSocketCore(std::shared_ptr<SocketCore> core);
int getPosition(){
return position_;
}
//返回当前utp_context 的互斥锁
std::mutex& getUtpContextpMutex(){
return utpContextMutex_;
}
};
}
#endif //ARIA2LIBANDROIDPROJECT_UTPCONTEXTUSERDATA_H
#include "UtpContextUserData.h"
#include "DownloadEngine.h"
#include "m4399_log.h"
namespace aria2 {
//初始化函数
void UtpContextUserData::init(DownloadEngine * engine,int position){
downloadEngine = engine;
position_ = position;
}
DownloadEngine* UtpContextUserData::getDownloadEngine(){
return downloadEngine;
}
//根据指定的ip和端口号得到对应的连接对象
std::shared_ptr<SocketCore> UtpContextUserData::getConnection(std::string addr,uint16_t port) {
//1.std::lock_guard 在构造函数中进行加锁,析构函数中进行解锁。
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mutex_);
auto i = mapSocket.find(std::make_pair(addr, port));
if (i == mapSocket.end()) {
return NULL;
}
return (*i).second;
}
//将对应的端口号跟ip对应起来
void UtpContextUserData::putConnection(std::string addr, uint16_t port,std::shared_ptr<SocketCore> conn,std::string commandName) {
//1.std::lock_guard 在构造函数中进行加锁,析构函数中进行解锁。
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mutex_);
auto i = mapSocket.find(std::make_pair(addr, port));
if (i == mapSocket.end()) {
mapSocket[std::make_pair(addr, port)] = conn;
LOGD("UtpContextUserData putConnection commandName %s first addr %s port %d socket fd %d",commandName.c_str(),addr.c_str(),port,conn->getSockfd());
}else{
if((*i).second == conn){
return;
}
mapSocket[std::make_pair(addr, port)] = conn;
LOGD("UtpContextUserData putConnection commandName %s update addr %s port %d socket fd %d",commandName.c_str(),addr.c_str(),port,conn->getSockfd());
}
}
//将当前对应的ip和端口号,从集合里面移除出去
bool UtpContextUserData::deleteAddr(std::string addr,uint16_t port){
//1.std::lock_guard 在构造函数中进行加锁,析构函数中进行解锁。
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mutex_);
mapSocket.erase(std::make_pair(addr, port));
return false;
}
//添加socketCore 到队列中,由于这里只会在主线程中执行,不加锁
void UtpContextUserData::setSocketCore(std::shared_ptr<SocketCore> core){
socketCore_ = core;
}
//客户端随机的从队列里面获取到一个fd
std::shared_ptr<SocketCore> UtpContextUserData::clientGetConnection(){
return socketCore_;
}
}
当收到消息的时候保留这个对应的关系
//保存SocketCore 对应的ip关系
contextUserData->putConnection(remoteAddr,remotePort, readCheckSocket_,"BtRecvMessageCommand1");
结果
优化后的结果