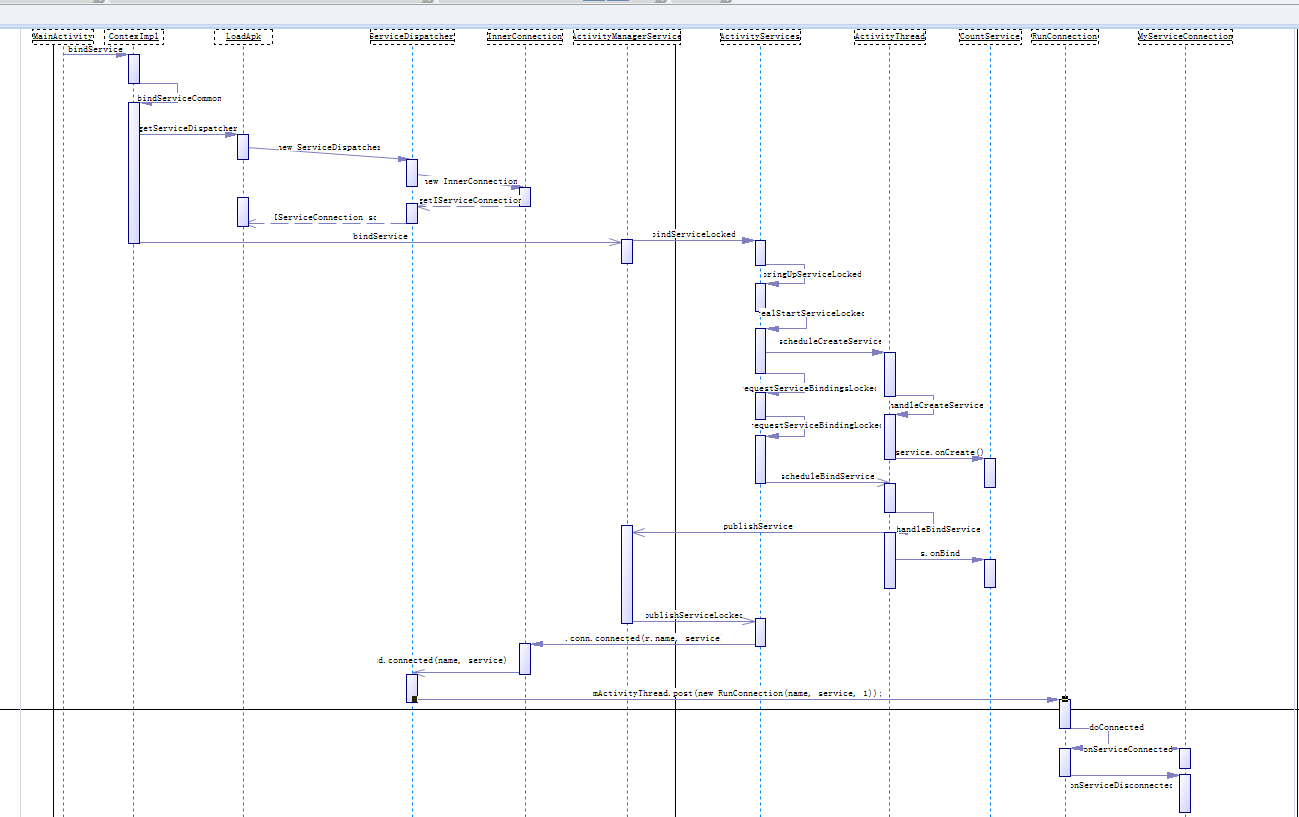
Android应用程序组件Service与Activity一样,既可以在新的进程中启动,也可以在应用程序进程内部启动;前面我们已经分析了在新的进程中启动Service的过程,
本文将要介绍在应用程序内部绑定Service的过程,这是一种在应用程序进程内部启动Service的方法。
案列书写方式
Intent bindIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, CounterServer.class);
bindService(bindIntent, serviceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Main Activity Created.");
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection()
{
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder)
{
//获取到service的接口
counterService = ((CounterServer.MyCounterBinder)iBinder).getCounterService();
Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Counter Service Connected");
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName)
{
counterService = null;
Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Counter Service Disconnected");
}
};
<service android:name=".CounterServer"/>
源码分析
执行了bindService(bindIntent, serviceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);就会执行到ContextWrapper类中对应的方法
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,int flags) {
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}
mBase 为Context实例,这里为contextImpl对象,所以会执行到对应的方法,这里传递的flags为Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, mMainThread.getHandler(),Process.myUserHandle());
}
这里的mMainThread是一个ActivityThread实例,在contextImpl中的定义为 final ActivityThread mMainThread;
通过它的getHandler函数可以获得一个Handler对象,有了这个Handler对象后,就可以把消息分发到ActivityThread所在的线程消息队列中去了,
后面我们将会看到这个用法,现在我们暂时不关注,只要知道这里从ActivityThread处获得了一个Handler并且保存在下面要介绍的ServiceDispatcher中去就可以了。
public final class ActivityThread {
......
final H mH = new H();
......
private final class H extends Handler {
......
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
......
}
......
}
......
final Handler getHandler() {
return mH;
}
......
}
这里返回的Handler是在ActivityThread类内部从Handler类继承下来的一个H类实例变量。bindService继续往下执行
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags, Handler handler, UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
if (conn == null) {
.....
}
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), handler, flags);
} else {
....
}
validateServiceIntent(service);
try {
IBinder token = getActivityToken();
if (token == null && (flags&BIND_AUTO_CREATE) == 0 && mPackageInfo != null
&& mPackageInfo.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion
< android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH) {
flags |= BIND_WAIVE_PRIORITY;
}
service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
if (res < 0) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to bind to service " + service);
}
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
这里同时将参数传递进来,flags为Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE,handler为ActivityThread中的H对象
调用mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher函数来获得一个IServiceConnection接口,这里的mPackageInfo的类型是LoadedApk,getOuterContext()为MainActivity 我们来看看它的getServiceDispatcher函数的实现
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c, Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> map = mServices.get(context);
if (map != null) {
sd = map.get(c);
}
if (sd == null) {
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>();
mServices.put(context, map);
}
map.put(c, sd);
} else {
sd.validate(context, handler);
}
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
传进来的参数context是一个MainActivity实例,先以它为Key值在mServices中查看一下,是不是已经存在相应的ServiceDispatcher实例,如果有了,就不用创建了,直接取出来。
在我们这个情景中,需要创建一个新的ServiceDispatcher。
ServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection conn,Context context, Handler activityThread, int flags) {
mIServiceConnection = new InnerConnection(this);
mConnection = conn;
mContext = context;
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mLocation = new ServiceConnectionLeaked(null);
mLocation.fillInStackTrace();
mFlags = flags;
}
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
....
}
在创建新的ServiceDispatcher实例的过程中,将上面传下来ServiceConnection参数c和Hanlder参数保存在了ServiceDispatcher实例的内部,
并且创建了一个InnerConnection对象,这是一个Binder对象,一会是要传递给ActivityManagerService的,ActivityManagerServic后续就是要通过这个Binder对象和ServiceConnection通信的。
sd.getIServiceConnection() 函数
IServiceConnection getIServiceConnection() {
return mIServiceConnection;
}
getServiceDispatcher最后就是返回了一个InnerConnection对象给ContextImpl.bindService函数。回到ContextImpl.bindService函数中,它接着就要调用ActivityManagerService的远程接口来进一步处理了。
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
首先会执行到ActivityManagerProxy中对应的方法
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection,
int flags, String callingPackage, int userId) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
service.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeStrongBinder(connection.asBinder());
data.writeInt(flags);
data.writeString(callingPackage);
data.writeInt(userId);
mRemote.transact(BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int res = reply.readInt();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
return res;
}
然后会执行到ActivityManagerService中对应的方法
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage,
int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("bindService");
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
if (callingPackage == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("callingPackage cannot be null");
}
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
然后执行mServices.bindServiceLocked()
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String callingPackage, final int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
......
synchronized(this) {
......
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
......
ActivityRecord activity = null;
if (token != null) {
activity = ActivityRecord.isInStackLocked(token);
if (activity == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Binding with unknown activity: " + token);
return 0;
}
}
......
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType,
Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid());
......
ServiceRecord s = res.record;
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
......
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent);
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = s.connections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>();
s.connections.put(binder, clist);
}
clist.add(c);
b.connections.add(c);
if (activity != null) {
if (activity.connections == null) {
activity.connections = new HashSet<ConnectionRecord>();
}
activity.connections.add(c);
}
b.client.connections.add(c);
clist = mServiceConnections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>();
mServiceConnections.put(binder, clist);
}
clist.add(c);
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
......
if (!bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), false)) {
return 0;
}
}
......
}
return 1;
}
......
}
函数首先根据传进来的参数token是MainActivity在ActivityManagerService里面的一个令牌,通过这个令牌就可以将这个代表MainActivity的ActivityRecord取回来了。
接着通过retrieveServiceLocked函数,得到一个ServiceRecord,这个ServiceReocrd描述的是一个Service对象,这里就是CounterService了,这是根据传进来的参数service的内容获得的。
回忆一下在MainActivity.onCreate函数绑定服务的语句:
Intent bindIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, CounterServer.class);
bindService(bindIntent, serviceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
分下下 retrieveServiceLocked()函数的实现
private ServiceLookupResult retrieveServiceLocked(Intent service,
String resolvedType, String callingPackage, int callingPid, int callingUid, int userId,
boolean createIfNeeded, boolean callingFromFg, boolean isBindExternal) {
ServiceMap smap = getServiceMap(userId);
final ComponentName comp = service.getComponent();
if (comp != null) {
r = smap.mServicesByName.get(comp);
}
....
sInfo = new ServiceInfo(sInfo);
sInfo.applicationInfo = new ApplicationInfo(sInfo.applicationInfo);
sInfo.applicationInfo.packageName = aInfo.packageName;
sInfo.applicationInfo.uid = aInfo.uid;
name = new ComponentName(aInfo.packageName, name.getClassName()); name.getClassName可以得到CountService
service.setComponent(name); 这里的service为Intent对象
.....
}
而我们在构建Intent的时候,调用了 new Intent(MainActivity.this, CounterServer.class);
public Intent(Context packageContext, Class<?> cls) {
mComponent = new ComponentName(packageContext, cls);所以我们传递进来的packageContext,跟cls会封装成一个ComponentName对象
}
接下来,就是把传进来的参数connection封装成一个ConnectionRecord对象。注意,这里的参数connection是一个Binder对象,它的类型是LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection,是前面创建的
后续ActivityManagerService就是要通过它来告诉MainActivity,CounterService已经启动起来了,因此,这里要把这个ConnectionRecord变量c保存下来,它保在在好几个地方,
都是为了后面要用时方便地取回来的,这里就不仔细去研究了,只要知道ActivityManagerService要使用它时就可以方便地把它取出来就可以了,具体后面我们再分析。
最后,传进来的参数flags的位Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE为1(参见上面MainActivity.onCreate函数调用bindService函数时设置的参数),因此,这里会调用bringUpServiceLocked函数进一步处理。
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
....
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (DEBUG_MU) Slog.v(TAG_MU, "bringUpServiceLocked: appInfo.uid=" + r.appInfo.uid
+ " app=" + app);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.versionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortName, e);
}
......
if (app == null && !permissionsReviewRequired) {
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
"service", r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
String msg = "Unable to launch app "
+ r.appInfo.packageName + "/"
+ r.appInfo.uid + " for service "
+ r.intent.getIntent() + ": process is bad";
Slog.w(TAG, msg);
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
return msg;
}
if (isolated) {
r.isolatedProc = app;
}
}
}
由于我们没有在程序的AndroidManifest.xml配置文件中设置CounterService的process属性值,因此,它默认就为application标签的process属性值,而application标签的process属性值也没有设置
于是,它们就默认为应用程序的包名了,即这里的appName的值为"demo.yuhui.org.broadcastdemo"。接下来根据appName和应用程序的uid值获得一个ProcessRecord记录,由于之前在启动MainActivity的时候,已经根据这个appName和uid值创建了一个ProcessReocrd对象(具体可以参考Android应用程序启动过程源代码分析一文),因此,这里取回来的app和app.thread均不为null,于是,就执行realStartServiceLocked函数来执行下一步操作了。
如果这里得到的ProcessRecord变量app为null,又是什么情况呢?在这种情况下,就会执行后面的startProcessLocked函数来创建一个新的进程,然后在这个新的进程中启动这个Service了,
因为是在同一个应用程序,所以执行 realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app) throws RemoteException {
......
r.app = app;
......
app.services.add(r);
......
try {
......
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo);
......
} finally {
......
}
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r);
......
}
这个函数执行了两个操作,一个是操作是调用app.thread.scheduleCreateService函数来在应用程序进程内部启动CounterService,这个操作会导致CounterService的onCreate函数被调用;
另一个操作是调用requestServiceBindingsLocked函数来向CounterService要一个Binder对象,这个操作会导致CounterService的onBind函数被调用。
这里,我们先沿着app.thread.scheduleCreateService这个路径分析下去,然后再回过头来分析requestServiceBindingsLocked的调用过程。这里的app.thread是一个Binder对象的远程接口,
类型为ApplicationThreadProxy。每一个Android应用程序进程里面都有一个ActivtyThread对象和一个ApplicationThread对象,其中是ApplicationThread对象是ActivityThread对象的一个成员变量,
是ActivityThread与ActivityManagerService之间用来执行进程间通信的
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token, ServiceInfo info,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
info.writeToParcel(data, 0);
compatInfo.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeInt(processState);
try {
mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_CREATE_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, null,IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
Log.e("CREATE_SERVICE", "Binder failure starting service; service=" + info);
throw e;
}
data.recycle();
}
最终会执行到ActivityThread中对应的方法
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
case CREATE_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, ("serviceCreate: " + String.valueOf(msg.obj)));
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
service.onCreate(); 这个函数的工作就是把CounterService类加载到内存中来,然后调用它的onCreate函数。
mServices.put(data.token, service);
.......
}
public class CounterService extends Service implements ICounterService {
......
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Counter Service Created.");
}
......
}
至此,应用程序绑定服务过程中的第一步MainActivity.bindService->CounterService.onCreate就完成了。
这一步完成之后,回到realStartServiceLocked函数中 执行下一个操作,即调用ActivityManagerService.requestServiceBindingsLocked函数,这个调用是用来执行CounterService的onBind函数的。
private final void requestServiceBindingsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
for (int i=r.bindings.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
IntentBindRecord ibr = r.bindings.valueAt(i);
if (!requestServiceBindingLocked(r, ibr, execInFg, false)) {
break;
}
}
}
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
// If service is not currently running, can't yet bind.
return false;
}
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
// Keep the executeNesting count accurate.
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Crashed while binding " + r, e);
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Crashed while binding " + r);
// Keep the executeNesting count accurate.
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
这里的参数r就是我们在前面创建的ServiceRecord了,它代表刚才已经启动了的CounterService。函数requestServiceBindingsLocked调用了requestServiceBindingLocked函数来处理绑定服务的操作,
而函数requestServiceBindingLocked又调用了app.thread.scheduleBindService函数执行操作,前面我们已经介绍过app.thread,它是一个Binder对象的远程接口,类型是ApplicationThreadProxy。
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent, boolean rebind,
int processState) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeInt(rebind ? 1 : 0);
data.writeInt(processState);
mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, null,
IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
data.recycle();
}
之后会调用到最终的实现类这里即为ActivityThread中对应的方法即为
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent, boolean rebind, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "scheduleBindService token=" + token + " intent=" + intent + " uid="
+ Binder.getCallingUid() + " pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid());
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}
之后通过Handlerd回应执行
case BIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceBind");
handleBindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
private final void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
......
}
......
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
}
}
}
在前面执行ActivityThread.handleCreateService函数中,已经将这个CounterService实例保存在mServices中,在ActivityThrad中的handlerCreate()函数中有这样的语句
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
因此,这里首先通过data.token值将它取回来,保存在本地变量s中,接着执行了两个操作,一个操作是调用s.onBind,即CounterService.onBind获得一个Binder对象,也即是调用到了我们的代码中的
private final IBinder binder = new MyCounterBinder();
private MyAsyncTask mTask;
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent)
{
return binder;
}
//binder对象,返回接口类型
public class MyCounterBinder extends Binder
{
pubic ICounterService getCounterService()
{
return CounterServer.this;
}
}
另一个操作就是把这个Binder对象传递给ActivityManagerService。调用响应的方法
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
......
synchronized(this) {
......
ServiceRecord r = (ServiceRecord)token;
......
......
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
if (r.connections.size() > 0) {
Iterator<ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>> it
= r.connections.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = it.next();
for (int i=0; i<clist.size(); i++) {
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
......
try {
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
}
}
}
}
......
}
}
}
这里传进来的参数token是一个ServiceRecord对象,它是在上面创建的,代表CounterService这个Service,我们曾经把一个ConnectionRecord放在ServiceRecord.connections列表中:
ServiceRecord s = res.record;
......
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent);
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = s.connections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>();
s.connections.put(binder, clist);
}
因此,这里可以从r.connections中将这个ConnectionRecord取出来:
Iterator<ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>> it = r.connections.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = it.next();
for (int i=0; i<clist.size(); i++) {
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
......
try {
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
}
每一个ConnectionRecord里面都有一个成员变量conn,它的类型是IServiceConnection,是一个Binder对象的远程接口,这个Binder对象又是什么呢?这就是我们在前面创建的
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection对象了。因此,这里执行c.conn.connected函数后就会进入到LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection.connected函数中去了。
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
这里它将操作转发给ServiceDispatcher.connected函数。
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if(mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0));
} else {
doConnected(name, service);
}
}
我们在前面说到,这里的mActivityThread是一个Handler实例,它是通过ActivityThread.getHandler函数得到的,因此,调用它的post函数后,就会把一个消息放到ActivityThread的消息队列中去了。
private final class RunConnection implements Runnable {
RunConnection(ComponentName name, IBinder service, int command) {
mName = name;
mService = service;
mCommand = command;
}
public void run() {
if (mCommand == 0) {
doConnected(mName, mService);
} else if (mCommand == 1) {
doDeath(mName, mService);
}
}
final ComponentName mName;
final IBinder mService;
final int mCommand;
}
这里的mCommand值为0,于是就执行ServiceDispatcher.doConnected函数来进一步操作了。
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
......
// If there was an old service, it is now disconnected.
if (old != null) {
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
// If there is a new service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
}
这里主要就是执行成员变量mConnection的onServiceConnected函数,这里的mConnection变量的类型的ServiceConnection,它是在前面中设置好的,这个ServiceConnection实例是MainActivity类内部创建的,
在调用bindService函数时保存在LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher类中,用它来换取一个IServiceConnection对象,传给ActivityManagerService。也是就会到我们车间的ServiceConnection对象
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection()
{
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder)
{
/获取到service的接口
counterService = ((CounterServer.MyCounterBinder)iBinder).getCounterService();
Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Counter Service Connected");
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName)
{
counterService = null;
Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Counter Service Disconnected");
}
};
流程图