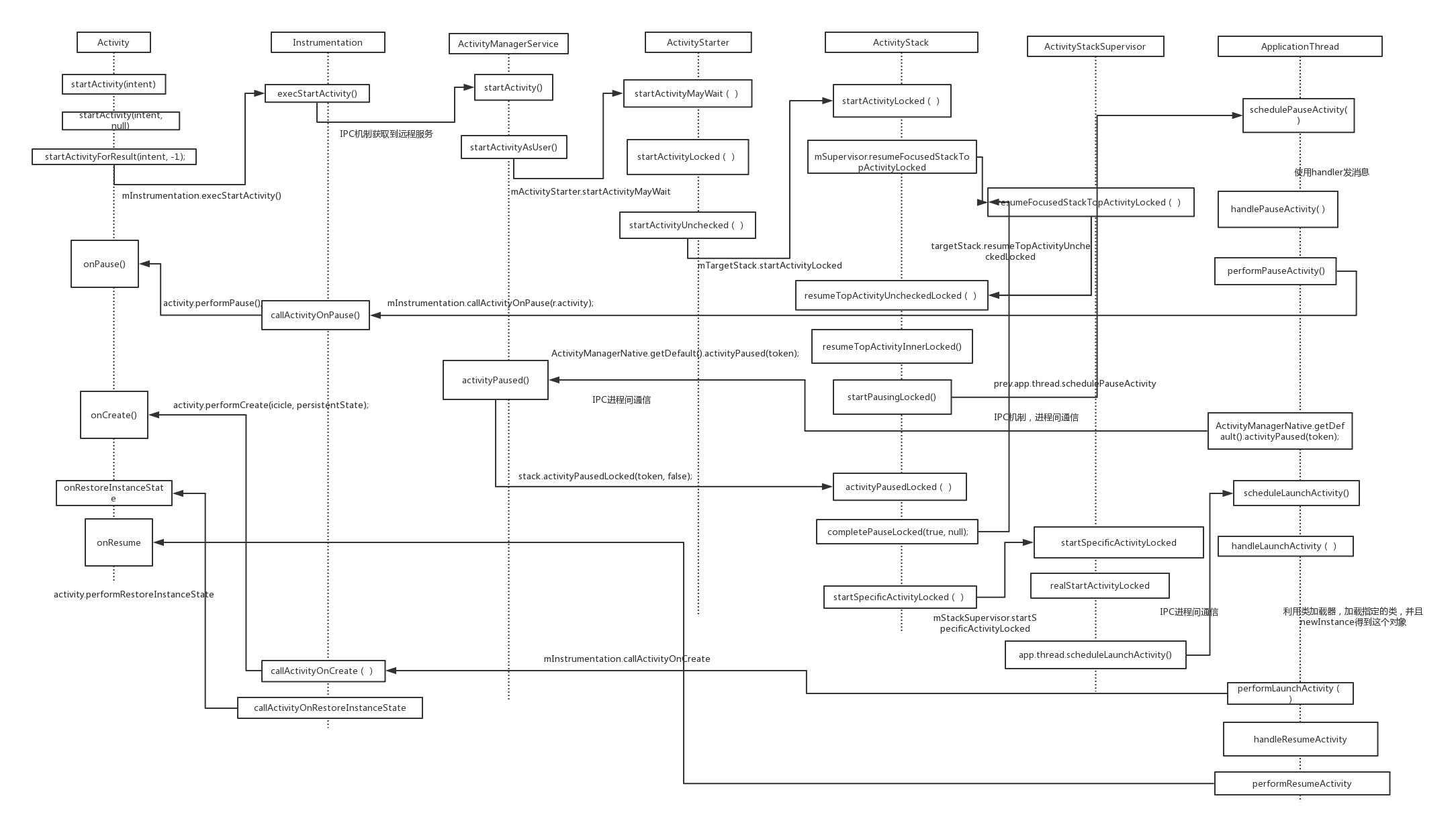
分析startActivity(new Intent())执行过程
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent) {
this.startActivity(intent, null);
}
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent, @Nullable Bundle options) {//根据this.startActivity(intent, null); 知道第二个参数传递的为null
if (options != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1, options);
} else {
// Note we want to go through this call for compatibility with
// applications that may have overridden the method.
startActivityForResult(intent, -1);//所以会执行到这里
}
}
public void startActivityForResult(@RequiresPermission Intent intent, int requestCode) {
startActivityForResult(intent, requestCode, null);
}
public void startActivityForResult(@RequiresPermission Intent intent, int requestCode,
....
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
intent, requestCode, options);
}
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
.....
int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, options);
....
}
static public IActivityManager getDefault() {
return gDefault.get();
}
private static final Singleton<IActivityManager> gDefault = new Singleton<IActivityManager>() {
protected IActivityManager create() {
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("activity");
if (false) {
Log.v("ActivityManager", "default service binder = " + b);
}
IActivityManager am = asInterface(b);//获取到IActivityManager IBinder对象
if (false) {
Log.v("ActivityManager", "default service = " + am);
}
return am;
}
};
asInterface(b);//获取到IActivityManager IBinder对象
static public IActivityManager asInterface(IBinder obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return null;
}
IActivityManager in = (IActivityManager)obj.queryLocalInterface(descriptor);//这边会查询是否是本进程之内的,如果是直接返回本地的IActivityManager对象
if (in != null) {
return in;
}
//我们这里会执行到这里,也即是跨进程的
return new ActivityManagerProxy(obj);
}
//远程代理的Ibinder
class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager
{
public ActivityManagerProxy(IBinder remote)
{
//存储了远程的Ibinder对象,也即是提供远程提供服务的类,这里其实就为ActivityManagerService
mRemote = remote;
}
public IBinder asBinder()
{
return mRemote;
}
}
//下面是ActivityManagerService类的关系,是间接继承 extends Binder implements IActivityManager
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
}
在Android 启动流程分析中,当启动了SystemService的时候,会启动ActivityMangaService,代码在 startBootstrapServices();函数中,理解IPC机制的知道当实现了IStub的或者IBinder
是用来提供服务的,也即是服务端的体现,实现了IProxy的是客户端的体现,客户端会持有远程的Ibinder 引用
所以当这边执行 ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()的时候,其实获取到的是ActivityManagerProxy对象,当执行了startActivity的时候
public int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage, Intent intent,
String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options) throws RemoteException {
.....
mRemote.transact(START_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
}
所以执行到mRemote.transact(START_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);的时候,就会执行到ActivityManagerService中的onTransact函数,这里是在父类也即是ActivityManagerNative中实现了
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case START_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION:
{
data.enforceInterface(IActivityManager.descriptor);
IBinder b = data.readStrongBinder();
IApplicationThread app = ApplicationThreadNative.asInterface(b);
String callingPackage = data.readString();
Intent intent = Intent.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
String resolvedType = data.readString();
IBinder resultTo = data.readStrongBinder();
String resultWho = data.readString();
int requestCode = data.readInt();
int startFlags = data.readInt();
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo = data.readInt() != 0
? ProfilerInfo.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data) : null;
Bundle options = data.readInt() != 0
? Bundle.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data) : null;
int result = startActivity(app, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType,
resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, options);
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(result);
return true;
}
......
}
当执行了startActivity()的时候,也即是执行到了ActivityManagerService中的方法,注意这已经是跨进程了
@Override
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,
resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, bOptions,
UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
@Override
public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions, int userId) {
......
// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.
return mActivityStarter.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent,
resolvedType, null, null, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags,
profilerInfo, null, null, bOptions, false, userId, null, null);
}
final int startActivityMayWait()
{
.......
return mActivityStarter.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent,
resolvedType, null, null, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags,
profilerInfo, null, null, bOptions, false, userId, null, null);
}
final int startActivityMayWait()
{
....
//得到当前意图对应的最合适的ResolveInfo对象
ResolveInfo rInfo = mSupervisor.resolveIntent(intent, resolvedType, userId);//查询Intent
// Collect information about the target of the Intent.
//获取到ActivityInfo ,这个成员是存储在rInfo中
ActivityInfo aInfo = mSupervisor.resolveActivity(intent, rInfo, startFlags, profilerInfo);
......
int res = startActivityLocked(caller, intent, ephemeralIntent, resolvedType,
aInfo, rInfo, voiceSession, voiceInteractor,
resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, callingPid,
callingUid, callingPackage, realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags,
options, ignoreTargetSecurity, componentSpecified, outRecord, container,
inTask);
}
//查询Intent
mSupervisor.resolveIntent(intent, resolvedType, userId);
ResolveInfo resolveIntent(Intent intent, String resolvedType, int userId) {
return resolveIntent(intent, resolvedType, userId, 0);
}
//查询Intent
ResolveInfo resolveIntent(Intent intent, String resolvedType, int userId, int flags) {
try {
return AppGlobals.getPackageManager().resolveIntent(intent, resolvedType,
PackageManager.MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY | flags
| ActivityManagerService.STOCK_PM_FLAGS, userId);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
return null;
}
AppGlobals.getPackageManager()执行的函数为
public static IPackageManager getPackageManager() {
return ActivityThread.getPackageManager();
}
//ActivityThread.getPackageManager(); 执行的函数为
public static IPackageManager getPackageManager() {
if (sPackageManager != null) {
//Slog.v("PackageManager", "returning cur default = " + sPackageManager);
return sPackageManager;
}
//可以发现这边得到的IPackageManager Ibinder对象
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("package");
//Slog.v("PackageManager", "default service binder = " + b);
sPackageManager = IPackageManager.Stub.asInterface(b); //这边又涉及到了IPC机制,源码分析中有讲解过PackageManagerService的启动过程
//Slog.v("PackageManager", "default service = " + sPackageManager);
return sPackageManager;
}
下面为PackageManagerService 的定义 public class PackageManagerService extends IPackageManager.Stub 可以看出他就是一个服务端,用来提供对象的,而且是主动的添加到ServiceManager中的
所以当执行到 AppGlobals.getPackageManager().resolveIntent()也即是执行到了PackageManagerService中的对应的函数,这又是跨进程
@Override
public ResolveInfo resolveIntent(Intent intent, String resolvedType,
int flags, int userId) {
try {
....
//大致就是查找意图对应的合适的一组对象,因为可能一个意图有多个对应的,,具体的细节自己查看
final List<ResolveInfo> query = queryIntentActivitiesInternal(intent, resolvedType,flags, userId);
//选择最合适的Activity
final ResolveInfo bestChoice = chooseBestActivity(intent, resolvedType, flags, query, userId);
return bestChoice;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_PACKAGE_MANAGER);
}
}
startActivityMayWait函数继续执行
int res = startActivityLocked(caller, intent, ephemeralIntent, resolvedType,
aInfo, rInfo, voiceSession, voiceInteractor,
resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, callingPid,
callingUid, callingPackage, realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags,
options, ignoreTargetSecurity, componentSpecified, outRecord, container,
inTask);
final int startActivityLocked(.....)
{
.....
验证intent、Class、Permission等
boolean abort = !mSupervisor.checkStartAnyActivityPermission(intent, aInfo, resultWho,
requestCode, callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage, ignoreTargetSecurity, callerApp,
resultRecord, resultStack, options);
保存将要启动的Activity的Record
ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, callerApp, callingUid, callingPackage,
intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.mConfiguration, resultRecord, resultWho,
requestCode, componentSpecified, voiceSession != null, mSupervisor, container,
options, sourceRecord);
.....
try {
mService.mWindowManager.deferSurfaceLayout();
err = startActivityUnchecked(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor, startFlags,
true, options, inTask);
} finally {
mService.mWindowManager.continueSurfaceLayout();
}
}
startActivityUnchecked() 就会执行到
private int startActivityUnchecked(.....)
{
......
mReusedActivity = setTargetStackAndMoveToFrontIfNeeded(mReusedActivity);//找到对应的activity的栈,并移动到前面
.....
mTargetStack.startActivityLocked(mStartActivity, newTask, mKeepCurTransition, mOptions);
....
mSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(mTargetStack, mStartActivity,mOptions);
}
setTargetStackAndMoveToFrontIfNeeded函数的实现
private ActivityRecord setTargetStackAndMoveToFrontIfNeeded(ActivityRecord intentActivity) {
......
//mSupervisor 是一个专门用来管理应用程序的栈的,这里就是获取到当前正在显示的应用程序的栈,
final ActivityStack focusStack = mSupervisor.getFocusedStack();
//如果当前的应用程序的栈不为空,获取当前显示的ActivityRecord对象,ActivityRecord里面存储了有关于Activity的所有的信息
ActivityRecord curTop = (focusStack == null)
? null : focusStack.topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(mNotTop);
.....
}
mSupervisor 是一个专门用来管理应用程序的栈的,每一个应用程序对应有一个栈,也即是ActivityStack对象,ActivityStack是用来
把所有的Activity按照先后顺序放在一个堆栈中,所以当我们按下返回键的时候,它会知道当前要显示哪个Activity,而mSupervisor是用来
管理应用程序的ActiviyStack的,所以它知道当你按下home键的时候,哪些应用程序要显示,哪些要隐藏,当你一直按后退键的时候
也知道哪一个应用程序将要显示,也即是对应的哪个ActivityStack将要显示,如果有newTask就会再创建一个栈,里面存储了我们应用程序的activity,而所有的应用对应的栈
又可以看成是一个小栈,是由mSupervisor来管理的,所以,这就是为什么但我们同时开启多个app,进入最后一个app,然后按返回键,为什么能看到其他的app界面的原因,我们没有做任何的处理
这都是由mSuperVisor来管理的,它将每一个应用程序的栈又做为一个栈的一个元素,当这个应用程序的栈从顶部移开的时候,那么下一个栈元素,也即是应用程序的栈,自动的会显示出来
mUpserVisor里面存储了一堆的集合来管理,比如那些界面是要进入pause状态,那些是要进入finish状态,哪些是要显示的状态
/** List of processes waiting to find out about the next visible activity. */
final ArrayList<IActivityManager.WaitResult> mWaitingActivityVisible = new ArrayList<>();
/** List of processes waiting to find out about the next launched activity. */
final ArrayList<IActivityManager.WaitResult> mWaitingActivityLaunched = new ArrayList<>();
/** List of activities that are ready to be stopped, but waiting for the next activity to
* settle down before doing so. */
final ArrayList<ActivityRecord> mStoppingActivities = new ArrayList<>();
/** List of activities that are ready to be finished, but waiting for the previous activity to
* settle down before doing so. It contains ActivityRecord objects. */
final ArrayList<ActivityRecord> mFinishingActivities = new ArrayList<>();
/** List of activities that are in the process of going to sleep. */
final ArrayList<ActivityRecord> mGoingToSleepActivities = new ArrayList<>();
/** List of activities whose multi-window mode changed that we need to report to the
* application */
final ArrayList<ActivityRecord> mMultiWindowModeChangedActivities = new ArrayList<>();
/** List of activities whose picture-in-picture mode changed that we need to report to the
* application */
final ArrayList<ActivityRecord> mPipModeChangedActivities = new ArrayList<>();
startActivityUnchecked函数继续执行,当执行到mTargetStack.startActivityLocked(mStartActivity, newTask, mKeepCurTransition, mOptions);
final void startActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean newTask, boolean keepCurTransition,
ActivityOptions options) {
....
task.addActivityToTop(r);//将当前的ActivityRecord记录添加到task顶部
task.setFrontOfTask();
....
r.putInHistory();//添加到历史的记录中
}
startActivityUnchecked函数继续执行,当执行到mSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(mTargetStack, mStartActivity,mOptions);
boolean resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(
ActivityStack targetStack, ActivityRecord target, ActivityOptions targetOptions) {
if (targetStack != null && isFocusedStack(targetStack)) {
return targetStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(target, targetOptions);
}
final ActivityRecord r = mFocusedStack.topRunningActivityLocked();
if (r == null || r.state != RESUMED) {
mFocusedStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(null, null);
}
return false;
}
当执行到targetStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(target, targetOptions);
boolean resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
......
result = resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options);
.....
}
private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
....
// We need to start pausing the current activity so the top one can be resumed... 就是在启动这个目标的activity之前要先将之前显示的activity,设置为pause状态
pausing |= startPausingLocked(userLeaving, false, next, dontWaitForPause);
......
}
//暂停显示的activity
final boolean startPausingLocked(boolean userLeaving, boolean uiSleeping,
ActivityRecord resuming, boolean dontWait) {
.....
prev.app.thread.schedulePauseActivity(prev.appToken, prev.finishing,//利用IPC,进车间通信
userLeaving, prev.configChangeFlags, dontWait);
...
}
这里的app.thread为 IApplicationThread thread ,而IApplicationThread 类的定义为 public interface IApplicationThread extends IInterface
它的服务端为/** {@hide} */ public abstract class ApplicationThreadNative extends Binder implements IApplicationThread 发现只是一个抽象类,它的最终实现为
private class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative
它的客户端为class ApplicationThreadProxy implements IApplicationThread ,
所以prev.app.thread,因为是跨进程调用,所以获取到的是ApplicationThreadProxy引用,所以就会调用对应的方法
public final void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
boolean userLeaving, int configChanges, boolean dontReport) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
data.writeInt(finished ? 1 : 0);
data.writeInt(userLeaving ? 1 :0);
data.writeInt(configChanges);
data.writeInt(dontReport ? 1 : 0);
mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_PAUSE_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, null,
IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
data.recycle();
}
执行 mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_PAUSE_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, null,IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);,就会调用到服务端具体的实现,也即是ApplicationThread中的
public final void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
boolean userLeaving, int configChanges, boolean dontReport) {
int seq = getLifecycleSeq();
if (DEBUG_ORDER) Slog.d(TAG, "pauseActivity " + ActivityThread.this
+ " operation received seq: " + seq);
sendMessage(
finished ? H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY_FINISHING : H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY,
token,
(userLeaving ? USER_LEAVING : 0) | (dontReport ? DONT_REPORT : 0),
configChanges,
seq);
}
sendMessage(finished ? H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY_FINISHING : H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY,
token,
(userLeaving ? USER_LEAVING : 0) | (dontReport ? DONT_REPORT : 0),
configChanges,
seq);
对应的handler 消息的处理为
case PAUSE_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityPause");
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs) msg.obj;
handlePauseActivity((IBinder) args.arg1, false,
(args.argi1 & USER_LEAVING) != 0, args.argi2,
(args.argi1 & DONT_REPORT) != 0, args.argi3);
maybeSnapshot();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
private void handlePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
boolean userLeaving, int configChanges, boolean dontReport, int seq) {
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
if (DEBUG_ORDER) Slog.d(TAG, "handlePauseActivity " + r + ", seq: " + seq);
if (!checkAndUpdateLifecycleSeq(seq, r, "pauseActivity")) {
return;
}
if (r != null) {
//Slog.v(TAG, "userLeaving=" + userLeaving + " handling pause of " + r);
if (userLeaving) {
performUserLeavingActivity(r);
}
r.activity.mConfigChangeFlags |= configChanges;
//最终会调用了Instruction中的 mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPause(r.activity); Instrumentation中callActivityOnPause实现为 activity.performPause(); 即回调了onPause
performPauseActivity(token, finished, r.isPreHoneycomb(), "handlePauseActivity");
// Make sure any pending writes are now committed.
if (r.isPreHoneycomb()) {
QueuedWork.waitToFinish();
}
// Tell the activity manager we have paused. 告知ActivityManagerService 我们已经暂停了
if (!dontReport) {
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityPaused(token);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
}
}
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityPaused(token);,这边会通过IPC机制,调用到ActivityManagerService远程服务端中对应的方法
@Override
public final void activityPaused(IBinder token) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
synchronized(this) {
// 获取到当前的ActivityStack栈
ActivityStack stack = ActivityRecord.getStackLocked(token);
if (stack != null) {
stack.activityPausedLocked(token, false);
}
}
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
stack.activityPausedLocked(token, false);
final void activityPausedLocked(IBinder token, boolean timeout) {
....
completePauseLocked(true, null);
......
}
private void completePauseLocked(boolean resumeNext, ActivityRecord resuming) {
....
mStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(topStack, prev, null);//恢复顶部获取焦点的activty
......
}
boolean resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked( ActivityStack targetStack, ActivityRecord target, ActivityOptions targetOptions) {
if (targetStack != null && isFocusedStack(targetStack)) {
return targetStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(target, targetOptions);
}
.....
}
boolean resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
....
result = resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options);
.....
}
private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
....
//如果有些activity的设置为单列模式的,就会执行newIntent
next.app.thread.scheduleNewIntent(
next.newIntents, next.appToken, false /* andPause */);
这里假设是正常的一个Activity
// Whoops, need to restart this activity!
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, false);//StackUpserVisor
...
}
//StackUpserVisor ,知道要启动哪个activity,暂停哪个Activity
void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
// Is this activity's application already running? 首先去检查当前要显示的Activity的应用程序是否正在运行,如果是通过启动界面进来的化,这里就会返回一个null
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo.uid, true);
r.task.stack.setLaunchTime(r);
//如果应用程序已经启动了,就直接启动指定的Activity
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
if ((r.info.flags&ActivityInfo.FLAG_MULTIPROCESS) == 0
|| !"android".equals(r.info.packageName)) {
// Don't add this if it is a platform component that is marked
// to run in multiple processes, because this is actually
// part of the framework so doesn't make sense to track as a
// separate apk in the process.
app.addPackage(r.info.packageName, r.info.applicationInfo.versionCode,
mService.mProcessStats);
}
realStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig);
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
}
//如果应用程序没有启动,就会来到这边
mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
"activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false, false, true);
}
下面是应用程序没有启动的情况
final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName,
ApplicationInfo info, boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags,
String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName, boolean allowWhileBooting,
boolean isolated, boolean keepIfLarge) {
return startProcessLocked(processName, info, knownToBeDead, intentFlags, hostingType,
hostingName, allowWhileBooting, isolated, 0 /* isolatedUid */, keepIfLarge,
null /* ABI override */, null /* entryPoint */, null /* entryPointArgs */,
null /* crashHandler */);
}
final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName, ApplicationInfo info,
boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags, String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName,
boolean allowWhileBooting, boolean isolated, int isolatedUid, boolean keepIfLarge,
String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs, Runnable crashHandler) {
long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
......
startProcessLocked(
app, hostingType, hostingNameStr, abiOverride, entryPoint, entryPointArgs);
......
}
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, String hostingType,
String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs) {
....
if (entryPoint == null) entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "Start proc: " +
app.processName);
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, app.info.seinfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, entryPointArgs);
.....
}
上面会通过Process.start的方式启动ActivityThread中的main函数,所以说每一个应用程序都有一个ActivityThread,它里面有一个主线程的Looper对象,一致循环执行,响应四大组件还有用户在主线程
通过handler发消息的作用,是很重要的
public static void main(String[] args) {
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
Looper.loop();
}
thread.attach(false);
private void attach(boolean system) {
....
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
.....
}
通过Binder机制调用到ActivityManagerService中对应的方法即为
@Override
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) {
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,int pid)
{
....
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, app.instrumentationClass,
profilerInfo, app.instrumentationArguments, app.instrumentationWatcher,
app.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(mConfiguration), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked());
...
// See if the top visible activity is waiting to run in this process...
if (normalMode) {
try {
if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown launching activities in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
}
thread.bindApplication()又会通过BINDER机制,执行到ActivityThread中对应的方法
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
List<ProviderInfo> providers, ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation,
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map<String, IBinder> services, Bundle coreSettings) {
AppBindData data = new AppBindData();
data.processName = processName;
data.appInfo = appInfo;
data.providers = providers;
data.instrumentationName = instrumentationName;
data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs;
data.instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher;
data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection = instrumentationUiConnection;
data.debugMode = debugMode;
data.enableBinderTracking = enableBinderTracking;
data.trackAllocation = trackAllocation;
data.restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode;
data.persistent = persistent;
data.config = config;
data.compatInfo = compatInfo;
data.initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo;
//发送系统的Hanlder
sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);
}
case BIND_APPLICATION:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "bindApplication");
AppBindData data = (AppBindData)msg.obj;
handleBindApplication(data);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
....
if (ii != null) {
final ApplicationInfo instrApp = new ApplicationInfo();
ii.copyTo(instrApp);
instrApp.initForUser(UserHandle.myUserId());
final LoadedApk pi = getPackageInfo(instrApp, data.compatInfo,
appContext.getClassLoader(), false, true, false);
final ContextImpl instrContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, pi);
try {
final ClassLoader cl = instrContext.getClassLoader();
mInstrumentation = (Instrumentation)
cl.loadClass(data.instrumentationName.getClassName()).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate instrumentation "
+ data.instrumentationName + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
final ComponentName component = new ComponentName(ii.packageName, ii.name);
mInstrumentation.init(this, instrContext, appContext, component,
data.instrumentationWatcher, data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection);
if (mProfiler.profileFile != null && !ii.handleProfiling
&& mProfiler.profileFd == null) {
mProfiler.handlingProfiling = true;
final File file = new File(mProfiler.profileFile);
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
Debug.startMethodTracing(file.toString(), 8 * 1024 * 1024);
}
} else {
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
}
...
try {
mInstrumentation.onCreate(data.instrumentationArgs);
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Exception thrown in onCreate() of "
+ data.instrumentationName + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
try {
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
上面做的操作即是通过类加载器,加载到Instruction,创建这个对象,Application对象,然后回掉执行对应的函数,比如
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
public void callApplicationOnCreate(Application app) {
app.onCreate();//即是会回掉到Application中的onCreate函数
}
程序继续执行当执行到
mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)
boolean attachApplicationLocked(ProcessRecord app) throws RemoteException {
...
ActivityRecord hr = stack.topRunningActivityLocked();
if (hr != null) {
if (hr.app == null && app.uid == hr.info.applicationInfo.uid
&& processName.equals(hr.processName)) {
try {
if (realStartActivityLocked(hr, app, true, true)) {//这个就是跟启动了应用程序执行一样的逻辑,所以下面分析应用程序启动的时候,原理是一样的
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception in new application when starting activity "
+ hr.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
throw e;
}
}
}
}
下面是应用程序已经启动的情况
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, ProcessRecord app,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) throws RemoteException {//抛出RemoteException 说明里面涉及到了远程的跨进程的调用
...
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken,//设计到了远程的调用,这里的app.thread为ApplicationThreadProxy 跨进程的客户端
System.identityHashCode(r), r.info, new Configuration(mService.mConfiguration),
new Configuration(task.mOverrideConfig), r.compat, r.launchedFromPackage,
task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle, r.persistentState, results,
newIntents, !andResume, mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo);
}
// ApplicationThreadProxy
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, Configuration overrideConfig,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int procState, Bundle state, PersistableBundle persistentState,
List<ResultInfo> pendingResults, List<ReferrerIntent> pendingNewIntents,
boolean notResumed, boolean isForward, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) throws RemoteException {
.....
mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_LAUNCH_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, null,//mRemote 为提供范围的ApplicationThread对象
IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
.....
}
//在ApplicationThreadNative 中的onTransact回掉中有下面的方法
scheduleLaunchActivity(intent, b, ident, info, curConfig, overrideConfig, compatInfo,
referrer, voiceInteractor, procState, state, persistentState, ri, pi,
notResumed, isForward, profilerInfo);
就会执行到它的最终实现类ApplicationThread中
// we use token to identify this activity without having to send the
// activity itself back to the activity manager. (matters more with ipc)
@Override
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, Configuration overrideConfig,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int procState, Bundle state, PersistableBundle persistentState,
List<ResultInfo> pendingResults, List<ReferrerIntent> pendingNewIntents,
boolean notResumed, boolean isForward, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) {
.....
sendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r);//H为系统级别的Handler,是用来处理,响应四大组件声明周期的关键人物
}
handler消息的接受
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
final ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord) msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
handleLaunchActivity(r, null, "LAUNCH_ACTIVITY");
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent, String reason) {
....
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
...
//如果上面launchAcivity启动正常
r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
reportSizeConfigurations(r);
Bundle oldState = r.state;
//执行handleResumeActivity
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward,
!r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed, r.lastProcessedSeq, reason);
......
}
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
.....
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();//得到类加载器
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity( // mInstrumentation 中的函数 newActivity所做的就是 (Activity)cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();利用类加载器,加载这个类
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
...
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);//给这个Activity构建Application对象
if (activity != null) {
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity);
//得到当前类的title
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (r.overrideConfig != null) {
config.updateFrom(r.overrideConfig);
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
Window window = null;
if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) {
window = r.mPendingRemoveWindow;
r.mPendingRemoveWindow = null;
r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = null;
}
//这个attach设计到了Window的初始话操作,后面会讲解
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window);
if (customIntent != null) {
activity.mIntent = customIntent;
}
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null;
activity.mStartedActivity = false;
//设置Activity的主题
int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
if (theme != 0) {
activity.setTheme(theme);
}
activity.mCalled = false;
if (r.isPersistable()) {
//Instrucation 中的 callActivityOnCreate activity.performCreate(icicle, persistentState); 也就会执行到了Activity中的 oncreate回调 onCreate(icicle, persistentState);
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
}
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onCreate()");
}
r.activity = activity;
r.stopped = true;
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.performStart();
r.stopped = false;
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
if (r.isPersistable()) {
if (r.state != null || r.persistentState != null) {
//最终会回调执行到 Activity中的onRestoreInstanceState(savedInstanceState, persistentState);函数
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state,
r.persistentState);
}
} else if (r.state != null) {
//最终会回调执行到 Activity中的onRestoreInstanceState(savedInstanceState, persistentState);函数
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);
}
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.mCalled = false;
if (r.isPersistable()) {
//最终会执行到activity.onPostCreate(icicle, persistentState);,也即回调执行到了onPostCreate()声明周期函数
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state,
r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state);
}
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPostCreate()");
}
}
}
r.paused = true;
//添加到Activitys里面
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to start activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
handleLaunchActivity 函数继续执行,当执行到了
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward, !r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed, r.lastProcessedSeq, reason);
final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean clearHide, boolean isForward, boolean reallyResume, int seq, String reason)
{
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);//launch 的时候刚添加过
....
r = performResumeActivity(token, clearHide, reason);
...
}
public final ActivityClientRecord performResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean clearHide, String reason) {
....
r.activity.performResume();
....
}
final void performResume() {
....
// mResumed is set by the instrumentation
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnResume(this);
....
}
public void callActivityOnResume(Activity activity) {
activity.mResumed = true;
activity.onResume();//最终回调执行到了Activity中的onResumes生命周期方法
if (mActivityMonitors != null) {
synchronized (mSync) {
final int N = mActivityMonitors.size();
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
final ActivityMonitor am = mActivityMonitors.get(i);
am.match(activity, activity, activity.getIntent());
}
}
}
}
启动流程