继上一篇文章介绍 在frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java中main函数,继续往下执行,就该创建SystemServer
并且循环进入监听模式, 监听创建进程的请求
if (startSystemServer) { //startSysteServer为true
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
runSelectLoop(abiList); //接受应用的socket链接请求
closeServerSocket(); //当退出循环时,系统出现问题, 所以也要将server socket关闭.
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);执行细节
/**
* Prepare the arguments and fork for the system server process.
*/
private static boolean startSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName)
throws MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {
//.......
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] = { //准备启动System Server所需要的参数
"--setuid=1000", //设置用户的ID为1000,这个UID代表系统权限
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1032,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server", //进程的名字为system_server
"--runtime-args",
"com.android.server.SystemServer", //设置要启动的类名
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
//将数组分解成Arguments类型的对象,过程很简单
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args); //通过ZygoteConnection对参数进行封装
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
/* Request to fork the system server process */
//调用系统fork函数创建子进程,这个子进程就是sysytem_server
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) { //pid为0说明在子进程system_server中
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName); //等待zygote第二阶段
}
//在子进程system_server中调用了handleSystemServerProcess方法
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs); //运行SystemServer,之后SystemServer就与Zygote分道扬镳,在自己的进程中运行
}
//在父进程中返回
return true;
}
Zygote调用forkSystenServer函数来进行创建SystemServer进程,具体代码位置frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/Zygote.java
/* @return 0 if this is the child, pid of the child
* if this is the parent, or -1 on error.
*/
public static int forkSystemServer(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int debugFlags,
int[][] rlimits, long permittedCapabilities, long effectiveCapabilities) {
VM_HOOKS.preFork(); //将所有守护进程停止运行
int pid = nativeForkSystemServer( //调用native函数孵化进程
uid, gid, gids, debugFlags, rlimits, permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities);
// Enable tracing as soon as we enter the system_server.
if (pid == 0) {
Trace.setTracingEnabled(true); //进入SystemServer进程,可以输出trace
}
VM_HOOKS.postForkCommon(); //重新运行各个守护进程
return pid;
}
native private static int nativeForkSystemServer(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int debugFlags,
int[][] rlimits, long permittedCapabilities, long effectiveCapabilities);
通过JNI调用到native函数中,代码位置frameworks/base/core/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
由于采用了动态注册的方式
static const JNINativeMethod gMethods[] = {
{ "nativeForkAndSpecialize",
"(II[II[[IILjava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;[ILjava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)I",
(void *) com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkAndSpecialize },
{ "nativeForkSystemServer", "(II[II[[IJJ)I",
(void *) com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkSystemServer },
{ "nativeUnmountStorageOnInit", "()V",
(void *) com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeUnmountStorageOnInit }
};
RegisterMethodsOrDie(env, "com/android/internal/os/Zygote", gMethods, NELEM(gMethods));
所以 nativeForkSystemServer 函数对应的为下面的实现
static jint com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkSystemServer(
JNIEnv* env, jclass, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray gids,
jint debug_flags, jobjectArray rlimits, jlong permittedCapabilities,
jlong effectiveCapabilities) {
pid_t pid = ForkAndSpecializeCommon(env, uid, gid, gids, ///孵化进程
debug_flags, rlimits,
permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities,
MOUNT_EXTERNAL_DEFAULT, NULL, NULL, true, NULL,
NULL, NULL);
if (pid > 0) { //pid大于0为父进程, 检查子进程是否已经死掉
// The zygote process checks whether the child process has died or not.
ALOGI("System server process %d has been created", pid); //输出SystemServer进程信息
gSystemServerPid = pid;
// There is a slight window that the system server process has crashed
// but it went unnoticed because we haven't published its pid yet. So
// we recheck here just to make sure that all is well.
int status;
if (waitpid(pid, &status, WNOHANG) == pid) { //判断子进程是否死掉, 如果死掉重启zygote
ALOGE("System server process %d has died. Restarting Zygote!", pid);
RuntimeAbort(env, __LINE__, "System server process has died. Restarting Zygote!");
}
}
return pid;
}
调用底层进行fork system server,在JNI中主要通过函数ForkAndSpecializeCommon中调用fork()函数孵化SystemServer进程。
Fork函数其实就是使用Linux调用fork创建进程。如果创建出的进程pid为0,说明新进程为Zygote的子进程,系统会为他设置uid,gid等参数。
新创建进程的pid大于0的话,说明该进程为进程SystemServer的进程号,Zygote进程会检查一下该进程有没有died,如果进程died了就会重新启动Zygote进程。
SystemServer进程创建完成后,就会重新启动垃圾回收后台进程。之后回到ZygoteInit中,SystemServer进程就与Zygote进程正式分道扬镳,pid=0为子进程,以后的代码都运行在了SystemServer进程中了
ForkAndSpecializeCommon函数的实现为
static pid_t ForkAndSpecializeCommon(JNIEnv* env, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray javaGids,
jint debug_flags, jobjectArray javaRlimits,
jlong permittedCapabilities, jlong effectiveCapabilities,
jint mount_external,
jstring java_se_info, jstring java_se_name,
bool is_system_server, jintArray fdsToClose,
jstring instructionSet, jstring dataDir) {
SetSigChldHandler();
#ifdef ENABLE_SCHED_BOOST
SetForkLoad(true);
#endif
pid_t pid = fork(); //孵化进程
if (pid == 0) {
// The child process.
gMallocLeakZygoteChild = 1;
// Clean up any descriptors which must be closed immediately
DetachDescriptors(env, fdsToClose);
// Keep capabilities across UID change, unless we're staying root.
if (uid != 0) {
EnableKeepCapabilities(env);
}
//........
if (!is_system_server) {
int rc = createProcessGroup(uid, getpid());
if (rc != 0) {
if (rc == -EROFS) {
ALOGW("createProcessGroup failed, kernel missing CONFIG_CGROUP_CPUACCT?");
} else {
ALOGE("createProcessGroup(%d, %d) failed: %s", uid, pid, strerror(-rc));
}
}
}
SetGids(env, javaGids);
SetRLimits(env, javaRlimits);
//...
rc = selinux_android_setcontext(uid, is_system_server, se_info_c_str, se_name_c_str); //设置selinux安全上下文
//....
} else if (pid > 0) {
// the parent process
#ifdef ENABLE_SCHED_BOOST
// unset scheduler knob
SetForkLoad(false);
#endif
}
return pid;
}
} // anonymous namespace
当Zygote复制出新的进程时,系统会将该进程的名字赋值为system_server,我们可以通过ps命令查看。可以发现zygote的进程id为system_service的父进程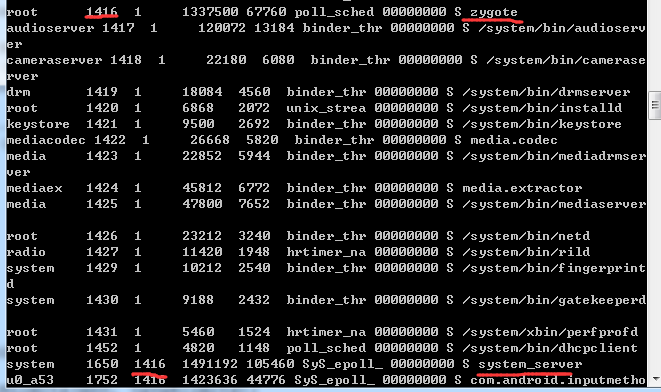
systemServerClasspath的内容为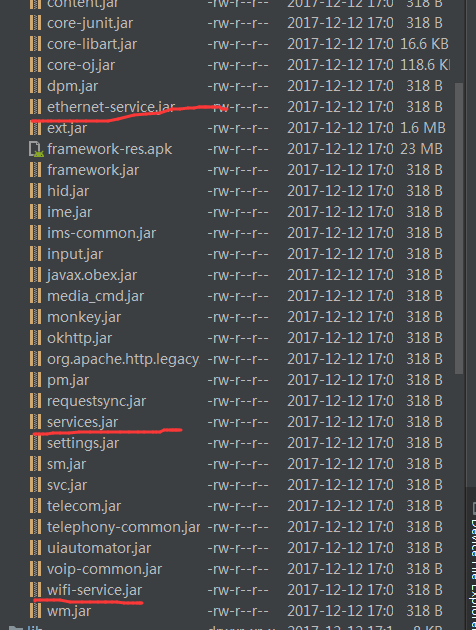
当Zygote复制出新的进程时,由于复制出的新进程与Zygote进程共享内存空间,而在Zygote进程中创建的服务端Socket是新进程不需要的,所以新创建的进程需要关闭该Socket服务端。
当Zygote复制出新的进程时,系统会将该进程的名字赋值为system_server,我们可以通过ps命令查看。
当startSystemServer函数 执行到 handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
private static void handleSystemServerProcess(
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
closeServerSocket(); //关闭zygote中的socket 这个是共享zygote进程出现的
// set umask to 0077 so new files and directories will default to owner-only permissions.
Os.umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);
if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName); //设置进程的名字 这里也即为system_server
}
//systemServerClasspath = /system/framework/services.jar:/system/framework/ethernet-service.jar:/system/framework/wifi-service.jar
final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH"); //获取systemServerClasspath
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
performSystemServerDexOpt(systemServerClasspath); //对该路径中的文件做dexopt优化
}
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) { //invokeWith为空故走else
String[] args = parsedArgs.remainingArgs;
// If we have a non-null system server class path, we'll have to duplicate the
// existing arguments and append the classpath to it. ART will handle the classpath
// correctly when we exec a new process.
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
String[] amendedArgs = new String[args.length + 2];
amendedArgs[0] = "-cp";
amendedArgs[1] = systemServerClasspath;
System.arraycopy(parsedArgs.remainingArgs, 0, amendedArgs, 2, parsedArgs.remainingArgs.length);
}
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(), null, args);
} else {
ClassLoader cl = null;
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
cl = createSystemServerClassLoader(systemServerClasspath,
parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion); //为systemServer创建ClassLoader, 让他可以进入平台的私有本地类库
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
/*
* Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
*/
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl); //调用到RuntimeInit中
}
/* should never reach here */
}
classPath中的内容为systemServerClasspath = /system/framework/services.jar:/system/framework/ethernet-service.jar:/system/framework/wifi-service.jar三个jar包,
之后会将这三个jar从路径中获取出来,判断是否要进行dexopt优化. 如果需要就调用installer进行优化. apk/jar
当执行到performSystemServerDexOpt的时候
/**
* Performs dex-opt on the elements of {@code classPath}, if needed. We
* choose the instruction set of the current runtime.
*/
private static void performSystemServerDexOpt(String classPath) {
final String[] classPathElements = classPath.split(":"); //将所需要优化的元素保存在string数组中
final InstallerConnection installer = new InstallerConnection();
installer.waitForConnection();
final String instructionSet = VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmInstructionSet();
try {
String sharedLibraries = "";
for (String classPathElement : classPathElements) {
// System server is fully AOTed and never profiled
// for profile guided compilation.
// TODO: Make this configurable between INTERPRET_ONLY, SPEED, SPACE and EVERYTHING?
final int dexoptNeeded = DexFile.getDexOptNeeded( //调用DexFile判断该元素是否要进行dexopt优化
classPathElement, instructionSet, "speed",
false /* newProfile */);
if (dexoptNeeded != DexFile.NO_DEXOPT_NEEDED) { //如果返回值不为NO_DEXOPT_NEEDED就进行优化
installer.dexopt(classPathElement, Process.SYSTEM_UID, instructionSet,
dexoptNeeded, 0 /*dexFlags*/, "speed", null /*volumeUuid*/,
sharedLibraries);
}
if (!sharedLibraries.isEmpty()) {
sharedLibraries += ":";
}
sharedLibraries += classPathElement;
}
} catch (IOException | InstallerException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error starting system_server", e);
} finally {
installer.disconnect();
}
}
当执行到
ClassLoader cl = null;
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
cl = createSystemServerClassLoader(systemServerClasspath,parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion))
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
根据systemServerClasspath创建classLoader, 最后,将启动SystemServer的参数解析完剩余的参数“com.android.server.SystemServer”保存在remainingArgs中,
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl);
并将参数传入RuntimeInit中。代码位置frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "RuntimeInit");
redirectLogStreams(); //初始化Android LOG输出流, 并且将system.out, system.err关闭, 将两者重新定向到Android log中
commonInit();//初始化运行环境
nativeZygoteInit(); //创建BInder线程池
applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}
当执行到 nativeZygoteInit();
private static final native void nativeZygoteInit(); //jni调用
通过JNI调用到AndroidRuntime.cpp中,代码位置framework/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
由于存在动态注册
/*
* JNI registration.
*/
static const JNINativeMethod gMethods[] = {
{ "nativeFinishInit", "()V",
(void*) com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeFinishInit },
{ "nativeZygoteInit", "()V",
(void*) com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeZygoteInit },
{ "nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup", "(Z)V",
(void*) com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup },
};
所以最终调用到
static void com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeZygoteInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{
gCurRuntime->onZygoteInit();
}
由于app_main.cpp为AndroidRuntime的子类, class AppRuntime : public AndroidRuntime
所以就调用到app_main中的onZygoteInit函数,具体代码位置frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp
virtual void onZygoteInit()
{
sp<ProcessState> proc = ProcessState::self(); //创建ProcessState
ALOGV("App process: starting thread pool.\n");
proc->startThreadPool(); //启动线程池
}
代码位置frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
void ProcessState::startThreadPool()
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
if (!mThreadPoolStarted) {
mThreadPoolStarted = true;
spawnPooledThread(true); //开始孵化线程池
}
}
void ProcessState::spawnPooledThread(bool isMain)
{
if (mThreadPoolStarted) { //变量为true
String8 name = makeBinderThreadName(); //获取binder的name
ALOGV("Spawning new pooled thread, name=%s\n", name.string());
sp<Thread> t = new PoolThread(isMain);
t->run(name.string()); //将binder放入线程池, 运行线程
}
}
String8 ProcessState::makeBinderThreadName() {
int32_t s = android_atomic_add(1, &mThreadPoolSeq);
pid_t pid = getpid(); //获取进程pid
String8 name;
name.appendFormat("Binder:%d_%X", pid, s); //为binder命名
return name;
}
之后继续执行 zygoteInit函数 调用applicationInit函数,继续向SystemServer中挺进.
private static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
//...........
final Arguments args;
try {
args = new Arguments(argv); //将argv参数封装到Argument中
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
Slog.e(TAG, ex.getMessage());
// let the process exit
return;
}
// The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit).
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader); //args.startClass为com.android.Server.SystemServer
}
在调用入口函数invokeStaticMain之前会将从ZygoteInit中传过来的参数进行处理,将com.android.server.SystemServer赋值给startClass,之后进入进程入口函数:
private static void invokeStaticMain(String className, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
Class<?> cl;
try {
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader); //通过反射获得SystemServer的class
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
Method m;
try {
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class }); //通过反射获取SystemServer的main函数
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers(); //获取main函数的修饰符
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) { //如果main函数不是静态公共的将会抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException(
"Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
/*
* This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
*/
throw new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv); //抛出异常到ZygoteInit,并传输参数
}
在函数执行最后抛出MethodAndArgsCaller异常,并在ZygoteInit.main中捕获该异常。这样就可以清除应用程序进程在创建过程中的调用栈。将应用程序入口设置为SystemServer的main函数。
public static void main(String argv[]) {
//.....
try {
//.....
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run(); //在函数中捕获异常, 并调用MethodAndArgsCaller的run函数
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);
closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}
其实MethodAndArgsCaller继承于Exception,并且实现于Runnable.
public static class MethodAndArgsCaller extends Exception
implements Runnable {
/** method to call */
private final Method mMethod; //要去调用的函数
/** argument array */
private final String[] mArgs; //参数组
public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {
mMethod = method; //构造函数, 将SystemServer的main函数赋值给mMethod
mArgs = args;
}
public void run() {
try {
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs }); //执行SystemServer的main函数, 从而进入到SystemServer中
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
} else if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
zygotefork进程的流程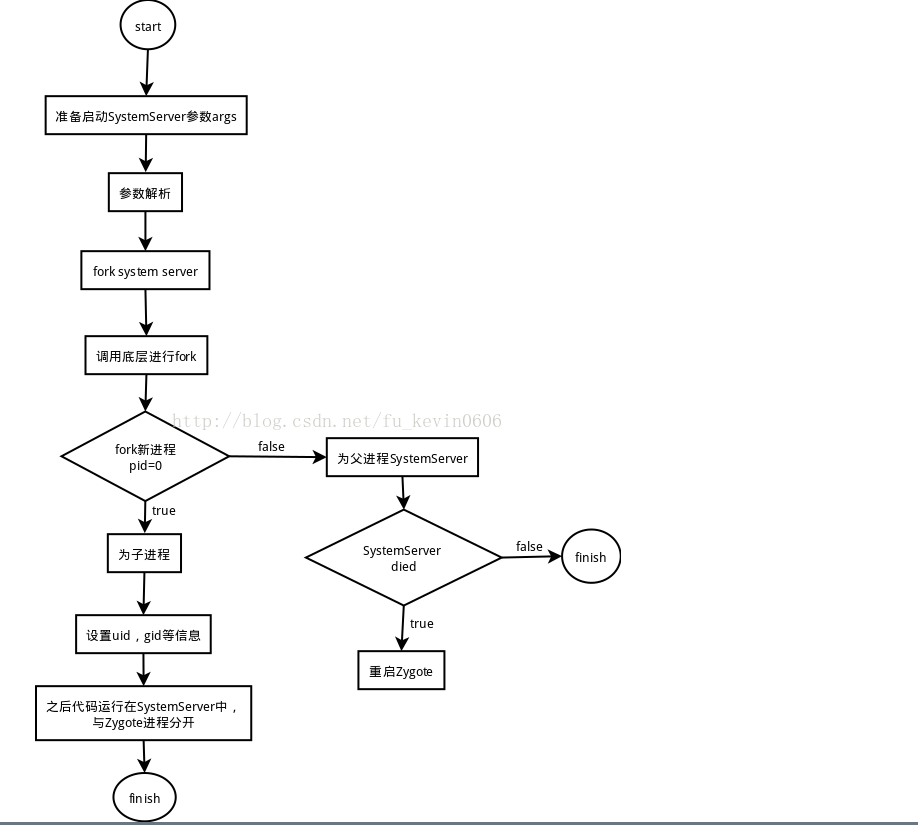
systemServerClasspath的内容为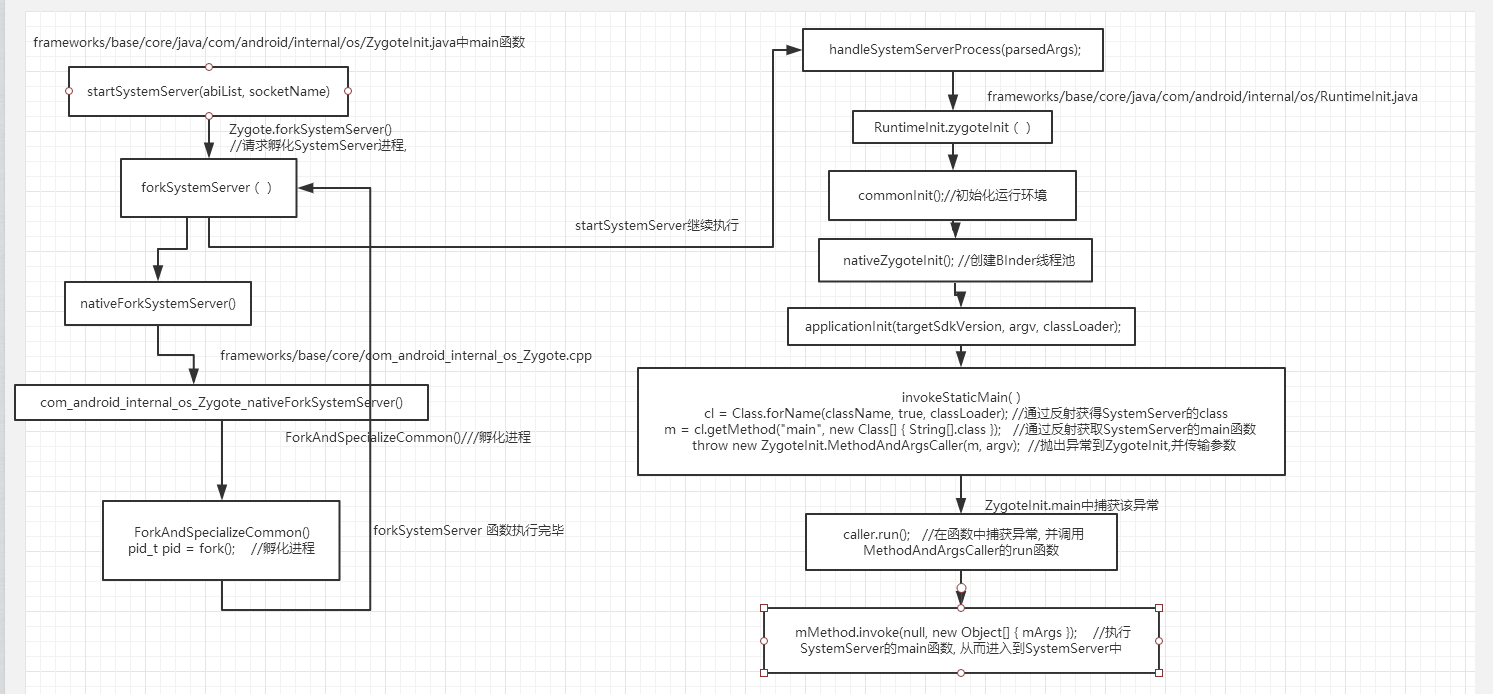
后文将继续讲解进入SystemServer后系统做了那些事情.



