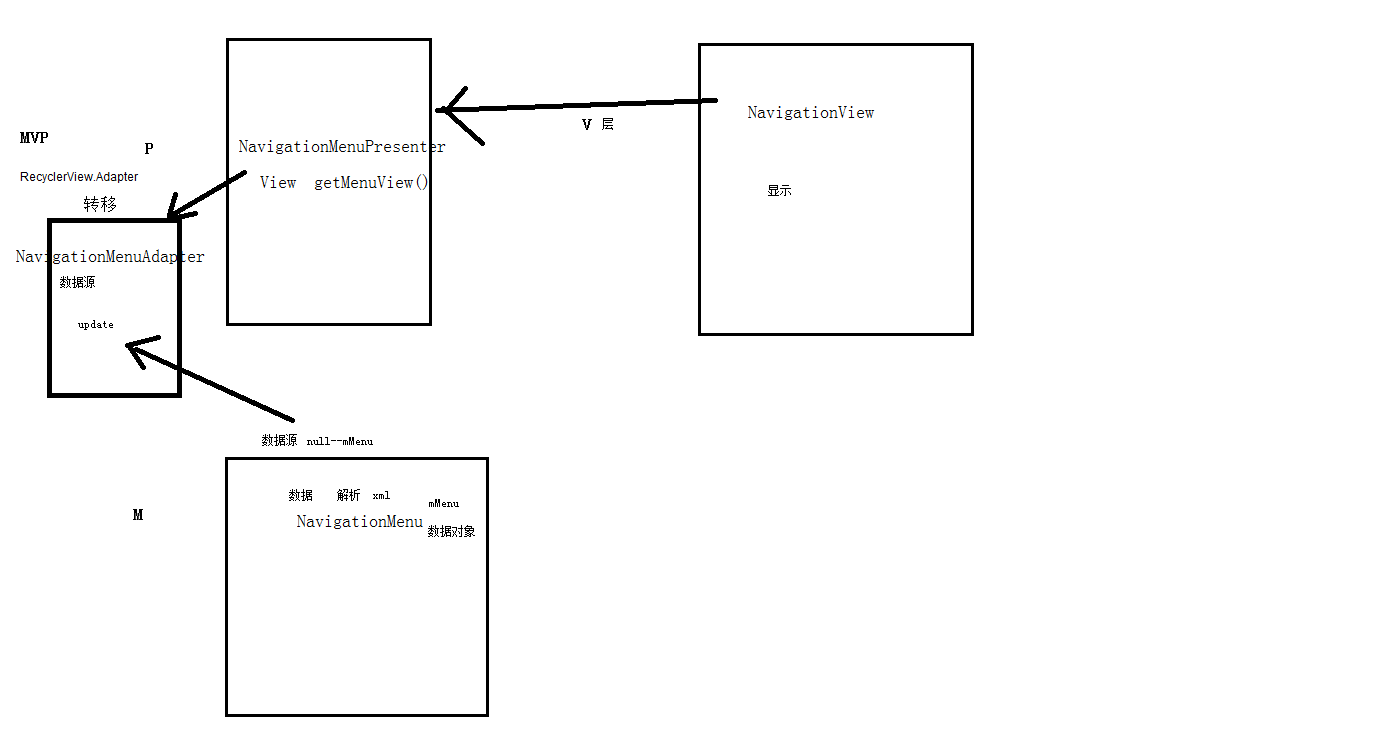
MVP的定义
在MVP里,Presenter完全把Model和View进行了分离,主要的程序逻辑在Presenter里实现。
而且,Presenter与具体的View是没有直接关联的,
而是通过定义好的接口进行交互,从而使得在变更View时候可以保持Presenter的不变。
View层显示功能,除此就不应该有更多的内容,绝不容许直接访问Model,这就是与MVC很大的不同之处。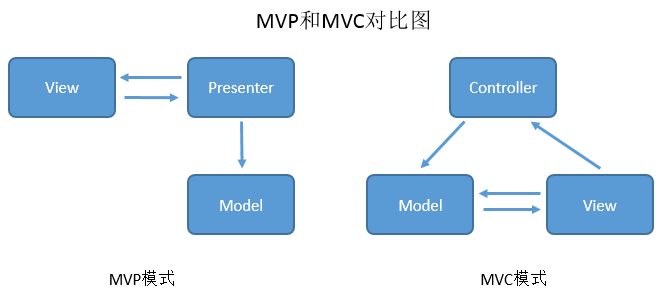
简单的使用
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.v4.widget.DrawerLayout
android:id="@+id/drawer"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
/>
<android.support.design.widget.NavigationView
android:id="@+id/navigation"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="start"
app:headerLayout="@layout/head" 左侧滑出菜单头部的布局
app:menu="@menu/view_menu" menu条目的布局
>
</android.support.design.widget.NavigationView>
</android.support.v4.widget.DrawerLayout>
layout/head
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/ivAvatar"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingTop="15dp"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_account_circle_white_48dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvNickName"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingTop="15dp"
tools:text="JohnTsai"
android:text="登录"
android:gravity="center"
android:textAppearance="@style/TextAppearance.AppCompat.Body1" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvRealName"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
tools:text="JohnTsaiAndroid" />
</LinearLayout>
menu/view_menu"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<group>
<item
android:id="@+id/nav_me"
android:title="我"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_mine_gray_24"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/nav_friend"
android:title="好友"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_friends_gray_24"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/nav_notification"
android:title="通知"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_notification_gray_24"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/nav_message"
android:title="私信"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_messages_gray_24"
/>
</group>
<menu>
运行结果为
源码分析
public class NavigationView extends ScrimInsetsFrameLayout {
MVP 中M层的实现
private final NavigationMenu mMenu;
MVP 中P层的实现 ,一上来就直接的初始话了一个全局的变量
private final NavigationMenuPresenter mPresenter = new NavigationMenuPresenter();
构造函数的执行
public NavigationView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
......
// Create the menu
mMenu = new NavigationMenu(context);
......
MVP中,M层持有了P层的引用
mMenu.addMenuPresenter(mPresenter);
这边可以推导p层是用来构建视图的
addView((View) mPresenter.getMenuView(this));
.....
这个为我们在使用NavigationView的时候,设置的menu布局文件
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.NavigationView_menu)) {
inflateMenu(a.getResourceId(R.styleable.NavigationView_menu, 0));
}
这个为我们在使用NavigationView的时候,设置的headerLayout布局文件
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.NavigationView_headerLayout)) {
inflateHeaderView(a.getResourceId(R.styleable.NavigationView_headerLayout, 0));
}
}
}
mPresenter.getMenuView(this));源码体现为
@Override
public MenuView getMenuView(ViewGroup root) {
if (mMenuView == null) {
发现public class NavigationMenuView extends RecyclerView implements MenuView 其实NavigationMenuView就是一个RecycleView
第三个参数为false,代表当前没有填充进root里面
mMenuView = (NavigationMenuView) mLayoutInflater.inflate(
R.layout.design_navigation_menu, root, false);
既然上面的本质为RecycleView 所以这个适配器就为RecycleView.Adapter
private class NavigationMenuAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<ViewHolder>
if (mAdapter == null) {
mAdapter = new NavigationMenuAdapter();
}
初始话mHeaderLayout ,本质为一个LineLayout
第三个参数为false,代表当前没有填充进mMenuView里面
mHeaderLayout = (LinearLayout) mLayoutInflater
.inflate(R.layout.design_navigation_item_header,
mMenuView, false);
给RecycleView 配置适配器
mMenuView.setAdapter(mAdapter);
}
return mMenuView;
}
R.layout.design_navigation_menu 布局文件为
<android.support.design.internal.NavigationMenuView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/design_navigation_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/design_navigation_padding_bottom"
android:clipToPadding="false"
android:scrollbars="vertical"/>
R.layout.design_navigation_item_header布局文件为
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/navigation_header_container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/design_navigation_separator_vertical_padding" />
首先分析 inflateMenu(a.getResourceId(R.styleable.NavigationView_menu, 0));的实现过程
public void inflateMenu(int resId) {
mPresenter.setUpdateSuspended(true);
resId为我们使用的menu布局的id,这边做的事情就是传递mMenu进去,然后解析这个布局文件,将内容设置到mMenu里面,mMenu为我们的M层,用来处理数据的
getMenuInflater().inflate(resId, mMenu);
mPresenter.setUpdateSuspended(false);
上面的数据解析完之后,通知p层来构建视图
mPresenter.updateMenuView(false);
}
mPresenter.updateMenuView(false); 源码实现为
@Override
public void updateMenuView(boolean cleared) {
if (mAdapter != null) {
mAdapter.update();
}
}
public void update() {
填充内容的布局
prepareMenuItems();
然后通知刷新界面
notifyDataSetChanged();
}
/**
* Flattens the visible menu items of {@link #mMenu} into {@link #mItems},
* while inserting separators between items when necessary.
*/
private void prepareMenuItems() {
if (mUpdateSuspended) {
return;
}
// private final ArrayList<NavigationMenuItem> mItems = new ArrayList<>(); 为适配器中要构建的item
mUpdateSuspended = true;
mItems.clear();
添加头部的Item
mItems.add(new NavigationMenuHeaderItem());
这边就会将mMenu的内容添加到mItems里面
for (int i = 0, totalSize = mMenu.getVisibleItems().size(); i < totalSize; i++) {
MenuItemImpl item = mMenu.getVisibleItems().get(i);
}
}
分析 inflateHeaderView(a.getResourceId(R.styleable.NavigationView_headerLayout, 0));
public View inflateHeaderView(@LayoutRes int res) {
P层用来构建试图
return mPresenter.inflateHeaderView(res);
}
mPresenter.inflateHeaderView(res);源码实现为
public View inflateHeaderView(@LayoutRes int res) {
加载一开始在布局文件里设置的header布局,这里的第三个参数为false,代表没有添加到mHeaderLayout里面
View view = mLayoutInflater.inflate(res, mHeaderLayout, false);
addHeaderView(view);
return view;
}
public void addHeaderView(@NonNull View view) {
最终将解析的header布局添加到一开始加载进来的LineLayout里面
mHeaderLayout.addView(view);
// The padding on top should be cleared.
mMenuView.setPadding(0, 0, 0, mMenuView.getPaddingBottom());
}
NavigationView类结构图
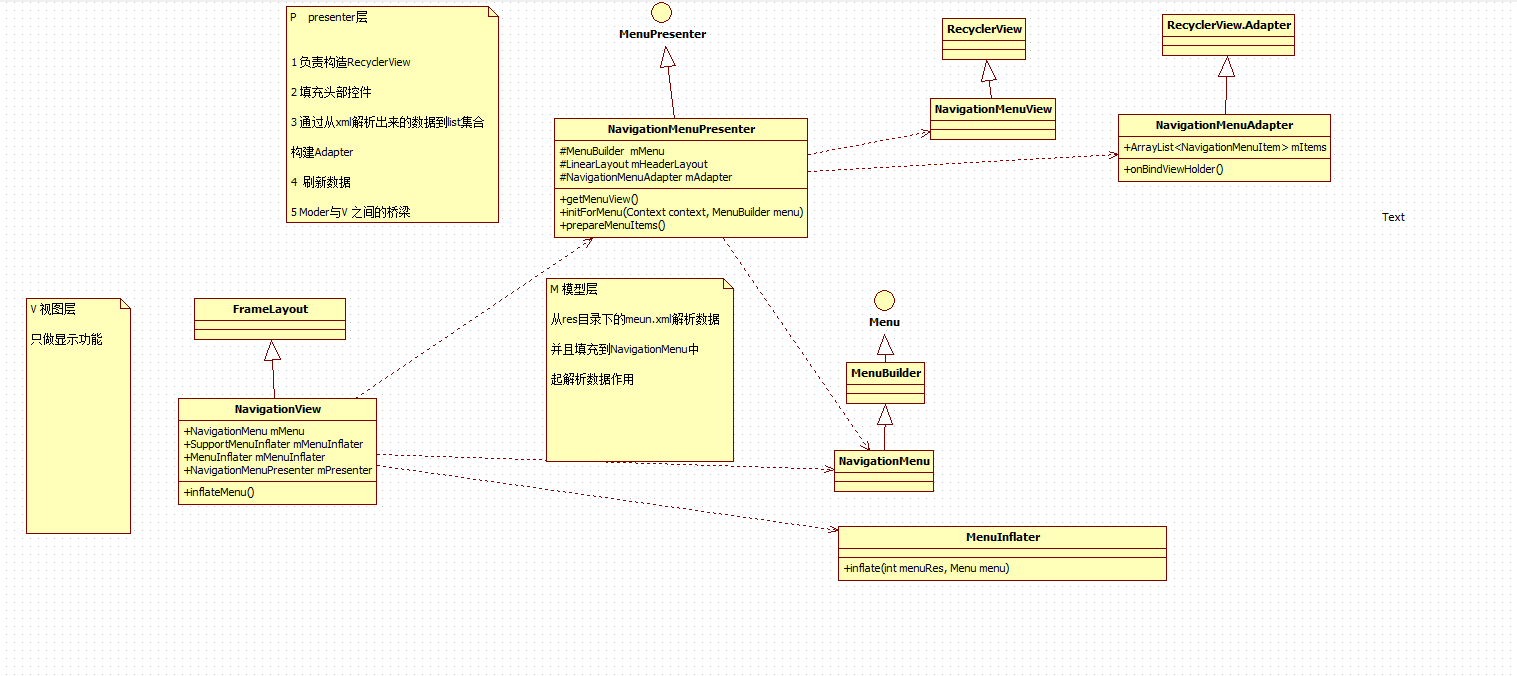
NavagitionView三层模型